Thymic stromal lymphopoietin: a new cytokine in asthma
- PMID: 18450510
- PMCID: PMC2518061
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2008.03.002
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin: a new cytokine in asthma
Abstract
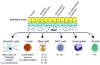
Airway epithelial cells provide mechanical and immune protection against pathogens and allergens. Following activation, these cells produce a wide range of cytokines including thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP). Recently it was established that a high level of TSLP is associated with asthma in mice and in humans. These findings suggest that interfering with the ability of cells to respond to TSLP might prevent the development of airway inflammation. Our review presents current knowledge on mediators that induce TSLP production and on the actions of TSLP on different populations of cells that are related to airway inflammation. TSLP affects dendritic cells, T cells, NKT cells, and mast cells, indicative of the broad role of TSLP in the regulation of inflammatory/allergic processes.
Figures

References
-
- Corry DB. Emerging immune targets for the therapy of allergic asthma. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2002;1:55–64. - PubMed
-
- Bloemen K, Verstraelen S, Van Den Heuvel R, Witters H, Nelissen I, Schoeters G. The allergic cascade: review of the most important molecules in the asthmatic lung. Immunol Lett. 2007;113:6–18. - PubMed
-
- Hart PH. Regulation of the inflammatory response in asthma by mast cell products. Immunol Cell Biol. 2001;79:149–153. - PubMed
-
- Cookson W. The immunogenetics of asthma and eczema: a new focus on the epithelium. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:978–988. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

