Cathepsin L is responsible for processing and activation of proheparanase through multiple cleavages of a linker segment
- PMID: 18450756
- PMCID: PMC2440611
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M801327200
Cathepsin L is responsible for processing and activation of proheparanase through multiple cleavages of a linker segment
Abstract
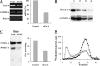
Heparanase is an endo-beta-d-glucuronidase that degrades heparan sulfate in the extracellular matrix and on the cell surface. Human proheparanase is produced as a latent protein of 543 amino acids whose activation involves excision of an internal linker segment (Ser(110)-Gln(157)), yielding the active heterodimer composed of 8- and 50-kDa subunits. Applying cathepsin L knock-out tissues and cultured fibroblasts, as well as cathepsin L gene silencing and overexpression strategies, we demonstrate, for the first time, that removal of the linker peptide and conversion of proheparanase into its active 8 + 50-kDa form is brought about predominantly by cathepsin L. Excision of a 10-amino acid peptide located at the C terminus of the linker segment between two functional cathepsin L cleavage sites (Y156Q and Y146Q) was critical for activation of proheparanase. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry demonstrates that the entire linker segment is susceptible to multiple endocleavages by cathepsin L, generating small peptides. Mass spectrometry demonstrated further that an active 8-kDa subunit can be generated by several alternative adjacent endocleavages, yielding the precise 8-kDa subunit and/or slightly elongated forms. Altogether, the mode of action presented here demonstrates that processing and activation of proheparanase can be brought about solely by cathepsin L. The critical involvement of cathepsin L in proheparanase processing and activation offers new strategies for inhibiting the prometastatic, proangiogenic, and proinflammatory activities of heparanase.
Figures
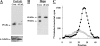
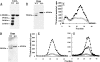
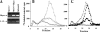


References
-
- Parish, C. R., Freeman, C., and Hulett, M. D. (2001) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1471 M99-M108 - PubMed
-
- Edovitsky, E., Elkin, M., Zcharia, E., Peretz, T., and Vlodavsky, I. (2004) J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 96 1219-1230 - PubMed
-
- Ilan, N., Elkin, M., and Vlodavsky, I. (2006) Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 38 2018-2039 - PubMed
-
- Nakajima, M., Irimura, T., and Nicolson, G. L. (1988) J. Cell. Biochem. 36 157-167 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

