Efficacy and tolerability of sevelamer carbonate in hyperphosphatemic patients who have chronic kidney disease and are not on dialysis
- PMID: 18450923
- PMCID: PMC2440270
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.05161107
Efficacy and tolerability of sevelamer carbonate in hyperphosphatemic patients who have chronic kidney disease and are not on dialysis
Abstract
Background and objectives: Sevelamer carbonate is an improved, buffered form of sevelamer hydrochloride developed for the treatment of hyperphosphatemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. This study investigated the ability of sevelamer carbonate to control serum phosphorous in hyperphosphatemic patients who had chronic kidney disease and were not on dialysis.
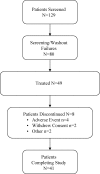
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: This was an open-label, dosage-titration study. Patients with serum phosphorus > or =5.5 mg/dl were enrolled (n = 46). Sevelamer carbonate was administered for 8 wk. Patients were supplemented with native vitamin D (400 IU). The primary efficacy parameter was the change from baseline in serum phosphorous. Secondary measures included the percentage of serum phosphorus responders; changes in serum lipids, calcium-phosphorus product, and bicarbonate; and safety and tolerability.
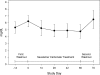
Results: Sevelamer carbonate treatment resulted in a statistically significant decrease in mean serum phosphorous levels from baseline to end of treatment. A total of 75% of patients with stage 4 and 70% of patients with stage 5 chronic kidney disease achieved the target serum phosphorous at the end of treatment. There were statistically significant decreases in serum calcium-phosphorus product and total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol at the end of treatment and a statistically significant increase in mean serum bicarbonate levels (from 16.6 to 18.2 mEq/L). Sevelamer carbonate was well tolerated.
Conclusions: Sevelamer carbonate is an effective and well-tolerated therapy for the control of phosphorous levels in hyperphosphatemic patients who have chronic kidney disease and are not on dialysis.
Figures
References
-
- Delmez JA, Slatopolsky E: Hyperphosphatemia: Its consequences and treatment in patients with chronic renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis 19: 303–317, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Young EW, Albert JM, Satayathum S, Goodkin DA, Pisoni RL, Akiba T, Akizawa T, Kurokawa K, Bommer J, Piera L, Port FK: Predictors and consequences of altered mineral metabolism: The Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study. Kidney Int 67: 1179–1187, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Slinin Y, Foley RN, Collins AJ: Calcium, phosphorus, parathyroid hormone, and cardiovascular disease in hemodialysis patients: The USRDS waves 1, 3, and 4 study. J Am Soc Nephrol 16: 1788–1793, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Block GA, Klassen PS, Lazarus JM, Ofsthun N, Lowrie EG, Chertow GM: Mineral metabolism, mortality, and morbidity in maintenance hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 2208–2218, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY: Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 351: 1296–1305, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical