Actively transcribed rRNA genes in S. cerevisiae are organized in a specialized chromatin associated with the high-mobility group protein Hmo1 and are largely devoid of histone molecules
- PMID: 18451108
- PMCID: PMC2335315
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.466908
Actively transcribed rRNA genes in S. cerevisiae are organized in a specialized chromatin associated with the high-mobility group protein Hmo1 and are largely devoid of histone molecules
Abstract
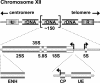
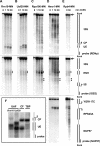
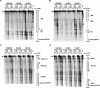
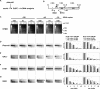
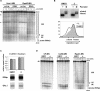
Synthesis of ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) is the major transcriptional event in proliferating cells. In eukaryotes, ribosomal DNA (rDNA) is transcribed by RNA polymerase I from a multicopy locus coexisting in at least two different chromatin states. This heterogeneity of rDNA chromatin has been an obstacle to defining its molecular composition. We developed an approach to analyze differential protein association with each of the two rDNA chromatin states in vivo in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We demonstrate that actively transcribed rRNA genes are largely devoid of histone molecules, but instead associate with the high-mobility group protein Hmo1.
Figures
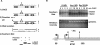
References
-
- Bell S.P., Learned R.M., Jantzen H.M., Tjian R. Functional cooperativity between transcription factors UBF1 and SL1 mediates human ribosomal RNA synthesis. Science. 1988;241:1192–1197. - PubMed
-
- Bell S.P., Jantzen H.M., Tjian R. Assembly of alternative multiprotein complexes directs rRNA promoter selectivity. Genes & Dev. 1990;4:943–954. - PubMed
-
- Bier M., Fath S., Tschochner H. The composition of the RNA polymerase I transcription machinery switches from initiation to elongation mode. FEBS Lett. 2004;564:41–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
