Use of complementary and alternative therapies by overweight and obese adults
- PMID: 18451783
- PMCID: PMC2776037
- DOI: 10.1038/oby.2008.239
Use of complementary and alternative therapies by overweight and obese adults
Abstract
Objective: Obesity is associated with higher health-care costs due, in part, to higher use of traditional health care. Few data are available on the relationship between obesity and the use of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM).
Methods and procedures: We analyzed data on CAM use from the 2002 National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) Alternative Medicine Supplement (n=31,044). We compared the use of CAM overall, within the past 12 months, between normal weight (BMI from 18 to <25), overweight (from 25 to <30), mildly obese (from 30 to <35), moderately obese (from 35 to <40), and extremely obese (>40) adults. For the primary analysis, our multivariable model was adjusted for sociodemographic factors, insurance status, medical conditions, and health behaviors. We performed additional analyses to explore the association of BMI and the use of seven CAM modalities.
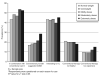
Results: We found that adults with obesity have lower prevalence of use of yoga therapy, and similar prevalence of use of several CAM modalities, including relaxation techniques, natural herbs, massage, chiropractic medicine, tai chi, and acupuncture, compared to normal-weight individuals. After adjustment for sociodemographic factors, insurance status, medical conditions, and health behaviors, adults with obesity were generally less likely to use most individual CAM modalities, although the magnitude of these differences were quite modest in many cases.
Discussion: Even though adults with obesity have a greater illness burden and higher utilization of traditional medical care, adults with higher BMIs were no more likely to use each of the individual CAM therapies studied. Additional research is needed to improve our understanding of CAM use by adults with obesity.
Figures
References
-
- Finkelstein EA, Fiebelkorn IC, Wang G. National medical spending attributable to overweight and obesity: how much, and who's paying? Health Aff (Millwood) 2003:W3-219–226. Suppl Web Exclusives. - PubMed
-
- Clegg DO, Reda DJ, Harris CL, et al. Glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, and the two in combination for painful knee osteoarthritis. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:795–808. - PubMed
-
- Thompson D, Wolf AM. The medical-care cost burden of obesity. Obes Rev. 2001;2:189–197. - PubMed
-
- Quesenberry CP, Jr, Caan B, Jacobson A. Obesity, health services use, and health care costs among members of a health maintenance organization. Arch Intern Med. 1998;158:466–472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous