How to perform meaningful estimates of genetic effects
- PMID: 18451979
- PMCID: PMC2320976
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000062
How to perform meaningful estimates of genetic effects
Abstract
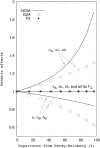
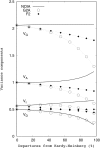
Although the genotype-phenotype map plays a central role both in Quantitative and Evolutionary Genetics, the formalization of a completely general and satisfactory model of genetic effects, particularly accounting for epistasis, remains a theoretical challenge. Here, we use a two-locus genetic system in simulated populations with epistasis to show the convenience of using a recently developed model, NOIA, to perform estimates of genetic effects and the decomposition of the genetic variance that are orthogonal even under deviations from the Hardy-Weinberg proportions. We develop the theory for how to use this model in interval mapping of quantitative trait loci using Halley-Knott regressions, and we analyze a real data set to illustrate the advantage of using this approach in practice. In this example, we show that departures from the Hardy-Weinberg proportions that are expected by sampling alone substantially alter the orthogonal estimates of genetic effects when other statistical models, like F2 or G2A, are used instead of NOIA. Finally, for the first time from real data, we provide estimates of functional genetic effects as sets of effects of natural allele substitutions in a particular genotype, which enriches the debate on the interpretation of genetic effects as implemented both in functional and in statistical models. We also discuss further implementations leading to a completely general genotype-phenotype map.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multiallelic models of genetic effects and variance decomposition in non-equilibrium populations.Genetica. 2011 Sep;139(9):1119-34. doi: 10.1007/s10709-011-9614-9. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Genetica. 2011. PMID: 22068562 Free PMC article.
-
A unified model for functional and statistical epistasis and its application in quantitative trait Loci analysis.Genetics. 2007 Jun;176(2):1151-67. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.067348. Epub 2007 Apr 3. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17409082 Free PMC article.
-
Orthogonal Estimates of Variances for Additive, Dominance, and Epistatic Effects in Populations.Genetics. 2017 Jul;206(3):1297-1307. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.199406. Epub 2017 May 18. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28522540 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation and interpretation of genetic effects with epistasis using the NOIA model.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;871:191-204. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-785-9_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22565838 Review.
-
Analysis of Epistasis in Natural Traits Using Model Organisms.Trends Genet. 2018 Nov;34(11):883-898. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2018.08.002. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Trends Genet. 2018. PMID: 30166071 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiallelic models of genetic effects and variance decomposition in non-equilibrium populations.Genetica. 2011 Sep;139(9):1119-34. doi: 10.1007/s10709-011-9614-9. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Genetica. 2011. PMID: 22068562 Free PMC article.
-
MAPfastR: quantitative trait loci mapping in outbred line crosses.G3 (Bethesda). 2013 Dec 9;3(12):2147-9. doi: 10.1534/g3.113.008623. G3 (Bethesda). 2013. PMID: 24122053 Free PMC article.
-
Two-stage genome-wide search for epistasis with implementation to Recombinant Inbred Lines (RIL) populations.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 23;9(12):e115680. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115680. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25536193 Free PMC article.
-
Natural and orthogonal model for estimating gene-gene interactions applied to cutaneous melanoma.Hum Genet. 2014 May;133(5):559-74. doi: 10.1007/s00439-013-1392-2. Epub 2013 Nov 17. Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24241239 Free PMC article.
-
A unified framework integrating parent-of-origin effects for association study.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 26;8(8):e72208. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072208. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23991061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carlborg Ö, Haley CS. Epistasis: too often neglected in complex trait studies? Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:618–625. - PubMed
-
- Hansen TF. The evolution of genetic architecture. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution and Systematics. 2006;37:123–157.
-
- Lynch M, Walsh B. Genetics and Analysis of Quantitative Traits. Sunderland: Sinauer; 1998.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

