Dynamic assessment of fibroblast mechanical activity during Rac-induced cell spreading in 3-D culture
- PMID: 18452153
- PMCID: PMC2663808
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.21487
Dynamic assessment of fibroblast mechanical activity during Rac-induced cell spreading in 3-D culture
Abstract
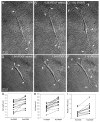
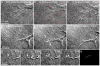
The goal of this study was to determine the morphological and sub-cellular mechanical effects of Rac activation on fibroblasts within 3-D collagen matrices. Corneal fibroblasts were plated at low density inside 100 microm thick fibrillar collagen matrices and cultured for 1-2 days in serum-free media. Time-lapse imaging was then performed using Nomarski DIC. After an acclimation period, perfusion was switched to media containing PDGF. In some experiments, Y-27632 or blebbistatin were used to inhibit Rho-kinase (ROCK) or myosin II, respectively. PDGF activated Rac and induced cell spreading, which resulted in an increase in cell length, cell area, and the number of pseudopodial processes. Tractional forces were generated by extending pseudopodia, as indicated by centripetal displacement and realignment of collagen fibrils. Interestingly, the pattern of pseudopodial extension and local collagen fibril realignment was highly dependent upon the initial orientation of fibrils at the leading edge. Following ROCK or myosin II inhibition, significant ECM relaxation was observed, but small displacements of collagen fibrils continued to be detected at the tips of pseudopodia. Taken together, the data suggests that during Rac-induced cell spreading within 3-D matrices, there is a shift in the distribution of forces from the center to the periphery of corneal fibroblasts. ROCK mediates the generation of large myosin II-based tractional forces during cell spreading within 3-D collagen matrices, however residual forces can be generated at the tips of extending pseudopodia that are both ROCK and myosin II-independent.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Role of Thrombin and Cell Contractility in Regulating Clustering and Collective Migration of Corneal Fibroblasts in Different ECM Environments.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015 Mar 3;56(3):2079-90. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-16388. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015. PMID: 25736789 Free PMC article.
-
Direct, dynamic assessment of cell-matrix interactions inside fibrillar collagen lattices.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2003 Aug;55(4):254-64. doi: 10.1002/cm.10126. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2003. PMID: 12845599
-
Corneal fibroblasts respond rapidly to changes in local mechanical stress.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004 Oct;45(10):3466-74. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-0361. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004. PMID: 15452051
-
Modulation of corneal fibroblast contractility within fibrillar collagen matrices.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003 Nov;44(11):4724-35. doi: 10.1167/iovs.03-0513. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003. PMID: 14578392
-
The shape of motile cells.Curr Biol. 2009 Sep 15;19(17):R762-71. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.06.053. Curr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19906578 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An In Vitro Model for Assessing Corneal Keratocyte Spreading and Migration on Aligned Fibrillar Collagen.J Funct Biomater. 2018 Sep 21;9(4):54. doi: 10.3390/jfb9040054. J Funct Biomater. 2018. PMID: 30248890 Free PMC article.
-
Squishy matters - Corneal mechanobiology in health and disease.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2024 Mar;99:101234. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2023.101234. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2024. PMID: 38176611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ECM stiffness modulates the proliferation but not the motility of primary corneal keratocytes in response to PDGF-BB.Exp Eye Res. 2022 Jul;220:109112. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.109112. Epub 2022 May 18. Exp Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 35595094 Free PMC article.
-
Regional mechanics determine collagen fiber structure in healing myocardial infarcts.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012 May;52(5):1083-90. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.02.012. Epub 2012 Mar 7. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22418281 Free PMC article.
-
Corneal Fibroblast Migration Patterns During Intrastromal Wound Healing Correlate With ECM Structure and Alignment.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015 Nov;56(12):7352-61. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-17978. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015. PMID: 26562169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott A. Biology’s new dimension. Nature. 2003;424:870–872. - PubMed
-
- Allingham JS, Smith R, Rayment I. The structural basis of blebbistatin inhibition and specificity for myosin II. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005;12:378–379. - PubMed
-
- Andresen JL, Ledet T, Ehlers N. Keratocyte migration and peptide growth factors: the effect of PDGF, bFGF, EGF, IGF-1, aFGF and TGF-beta on human keratocyte migration in a collagen gel. Curr Eye Res. 1997;16:605–613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

