Genome sequence and rapid evolution of the rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae PXO99A
- PMID: 18452608
- PMCID: PMC2432079
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-204
Genome sequence and rapid evolution of the rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae PXO99A
Erratum in
- BMC Genomics. 2008;9:534.. Seo, Young-Su [added]; Sriariyanum, Malinee [added]
Abstract
Background: Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae causes bacterial blight of rice (Oryza sativa L.), a major disease that constrains production of this staple crop in many parts of the world. We report here on the complete genome sequence of strain PXO99A and its comparison to two previously sequenced strains, KACC10331 and MAFF311018, which are highly similar to one another.
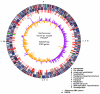
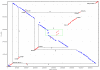
Results: The PXO99A genome is a single circular chromosome of 5,240,075 bp, considerably longer than the genomes of the other strains (4,941,439 bp and 4,940,217 bp, respectively), and it contains 5083 protein-coding genes, including 87 not found in KACC10331 or MAFF311018. PXO99A contains a greater number of virulence-associated transcription activator-like effector genes and has at least ten major chromosomal rearrangements relative to KACC10331 and MAFF311018. PXO99A contains numerous copies of diverse insertion sequence elements, members of which are associated with 7 out of 10 of the major rearrangements. A rapidly-evolving CRISPR (clustered regularly interspersed short palindromic repeats) region contains evidence of dozens of phage infections unique to the PXO99A lineage. PXO99A also contains a unique, near-perfect tandem repeat of 212 kilobases close to the replication terminus.
Conclusion: Our results provide striking evidence of genome plasticity and rapid evolution within Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. The comparisons point to sources of genomic variation and candidates for strain-specific adaptations of this pathogen that help to explain the extraordinary diversity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae genotypes and races that have been isolated from around the world.
Figures

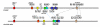



Similar articles
-
The genome sequence of Xanthomonas oryzae pathovar oryzae KACC10331, the bacterial blight pathogen of rice.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jan 26;33(2):577-86. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki206. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15673718 Free PMC article.
-
The rice bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae produces 3-hydroxybenzoic acid and 4-hydroxybenzoic acid via XanB2 for use in xanthomonadin, ubiquinone, and exopolysaccharide biosynthesis.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2013 Oct;26(10):1239-48. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-04-13-0112-R. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2013. PMID: 23718125
-
A two-genome microarray for the rice pathogens Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and X. oryzae pv. oryzicola and its use in the discovery of a difference in their regulation of hrp genes.BMC Microbiol. 2008 Jun 18;8:99. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-8-99. BMC Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18564427 Free PMC article.
-
Improved annotation of a plant pathogen genome Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae PXO99A.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2013 Mar;31(3):342-50. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2012.698218. Epub 2012 Aug 1. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2013. PMID: 22849520
-
Molecular determinants of disease and resistance in interactions of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and rice.Microbes Infect. 2002 Nov;4(13):1361-7. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(02)00004-7. Microbes Infect. 2002. PMID: 12443901 Review.
Cited by
-
Phylogenomics and molecular signatures for species from the plant pathogen-containing order xanthomonadales.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055216. Epub 2013 Feb 8. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23408961 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Thiamin Biosynthesis Genes in Rice Increases Leaf and Unpolished Grain Thiamin Content But Not Resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae.Front Plant Sci. 2016 May 10;7:616. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00616. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27242822 Free PMC article.
-
XA21-specific induction of stress-related genes following Xanthomonas infection of detached rice leaves.PeerJ. 2016 Sep 28;4:e2446. doi: 10.7717/peerj.2446. eCollection 2016. PeerJ. 2016. PMID: 27703843 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosomal Location of xa19, a Broad-Spectrum Rice Bacterial Blight Resistant Gene from XM5, a Mutant Line from IR24.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 29;12(3):602. doi: 10.3390/plants12030602. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771686 Free PMC article.
-
Rice xa13 recessive resistance to bacterial blight is defeated by induction of the disease susceptibility gene Os-11N3.Plant Cell. 2010 Nov;22(11):3864-76. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.078964. Epub 2010 Nov 23. Plant Cell. 2010. PMID: 21098734 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ou SH. Rice Diseases. 2. Kew, Surrey: Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau; 1985.
-
- Mew TW. Current status and future prospects of research on bacterial blight of rice. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 1987;25:359–382. doi: 10.1146/annurev.py.25.090187.002043. - DOI
-
- Leach JE, Leung H, Nelson RJ, Mew TW. Population biology of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and approaches to its control. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1995;6:298–304. doi: 10.1016/0958-1669(95)80051-4. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

