A proteomics approach for identification of single strand DNA-binding proteins involved in transcriptional regulation of mouse mu opioid receptor gene
- PMID: 18453338
- PMCID: PMC2494908
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M800052-MCP200
A proteomics approach for identification of single strand DNA-binding proteins involved in transcriptional regulation of mouse mu opioid receptor gene
Abstract
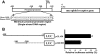
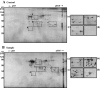
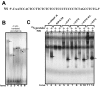
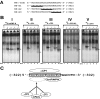
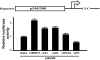
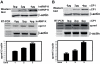
The pharmacological actions of morphine and morphine-like drugs such as heroin are mediated primarily through the mu opioid receptor. Previously a single strand DNA element of the mouse mu opioid receptor gene (Oprm1) proximal promoter was found to be important for regulating Oprm1 in neuronal cells. To identify proteins binding to the single strand DNA element as potential regulators for Oprm1, affinity column chromatography with the single strand DNA element was performed using neuroblastoma NS20Y cells followed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. We identified five poly(C)-binding proteins: heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) K, alpha-complex proteins (alphaCP) alphaCP1, alphaCP2, alphaCP2-KL, and alphaCP3. Binding of these proteins to the single strand DNA element of Oprm1 was sequence-specific as confirmed by supershift assays. In cotransfection studies, hnRNP K, alphaCP1, alphaCP2, and alphaCP2-KL activated the Oprm1 promoter activity, whereas alphaCP3 acted as a repressor. Ectopic expression of hnRNP K, alphaCP1, alphaCP2, and alphaCP2-KL also led to activation of the endogenous Oprm1 transcripts, and alphaCP3 repressed endogenous Oprm1 transcripts. We demonstrate novel roles as transcriptional regulators in Oprm1 regulation for hnRNP K and alphaCP binding to the single strand DNA element.
Figures



References
-
- Wei, L. N., and Loh, H. H. ( 2002) Regulation of opioid receptor expression. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2, 69–75 - PubMed
-
- Kieffer, B. L. ( 1999) Opioids: first lessons from knockout mice. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 20, 19–26 - PubMed
-
- Law, P. Y., Wong, Y. H., and Loh, H. H. ( 2000) Molecular mechanisms and regulation of opioid receptor signaling. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 40, 389–430 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

