Cost-effectiveness of lung volume reduction surgery
- PMID: 18453346
- PMCID: PMC2645310
- DOI: 10.1513/pats.200707-095ET
Cost-effectiveness of lung volume reduction surgery
Abstract
Lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS) is a costly procedure that can improve quality and quantity of life. Given the prevalence of emphysema, the costs involved with its management, and resource constraints on all health care delivery systems, evaluating the cost-effectiveness of LVRS is important. In this article, we describe the purposes and principles of cost-effectiveness analysis and how those principles were applied in evaluating LVRS. We present the results of the cost-effectiveness analysis that was conducted alongside the National Emphysema Treatment Trial and other economic studies of LVRS and discuss how these should be interpreted in the context of current reimbursement guidelines.
Figures
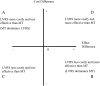
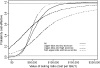
Similar articles
-
Cost effectiveness of lung volume reduction surgery.Chest Surg Clin N Am. 2003 Nov;13(4):727-38, vii-viii. doi: 10.1016/s1052-3359(03)00097-8. Chest Surg Clin N Am. 2003. PMID: 14682605 Review.
-
Updated evaluation of the cost-effectiveness of lung volume reduction surgery.Chest. 2007 Mar;131(3):823-832. doi: 10.1378/chest.06-1790. Chest. 2007. PMID: 17356099 Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized clinical trial of lung volume reduction surgery versus best medical care for patients with advanced emphysema: a two-year study from Canada.Ann Thorac Surg. 2006 Jan;81(1):314-20; discussion 320-1. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.07.055. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006. PMID: 16368389 Clinical Trial.
-
Economic analysis of lung volume reduction surgery as part of the National Emphysema Treatment Trial. NETT Research Group.Ann Thorac Surg. 2001 Mar;71(3):995-1002. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(00)02283-9. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001. PMID: 11269488 Clinical Trial.
-
National Emphysema Treatment Trial: the major outcomes of lung volume reduction surgery in severe emphysema.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2008 May 1;5(4):393-405. doi: 10.1513/pats.200801-013ET. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2008. PMID: 18453345 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endobronchial valves for emphysema: an individual patient-level reanalysis of randomised controlled trials.BMJ Open Respir Res. 2017 Nov 2;4(1):e000214. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2017-000214. eCollection 2017. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2017. PMID: 29441206 Free PMC article.
-
Health-related quality of life in emphysema.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2008 May 1;5(4):561-6. doi: 10.1513/pats.200706-080ET. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2008. PMID: 18453372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Attitudes and access to lung volume reduction surgery for COPD: a survey by the British Thoracic Society.BMJ Open Respir Res. 2014 Apr 30;1(1):e000023. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2014-000023. eCollection 2014. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2014. PMID: 25478175 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Exacerbations in Hospitalized Patients From Admission to Discharge: A Comprehensive Review of Therapeutic Interventions.Cureus. 2023 Aug 18;15(8):e43694. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43694. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37724212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emphysema: time to say farewell to therapeutic nihilism.Thorax. 2014 Nov;69(11):973-5. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-205667. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Thorax. 2014. PMID: 24985493 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Flaherty KR, Kazerooni EA, Curtis JL, Iannettoni M, Lange L, Schork MA, Martinez FJ. Short-term and long-term outcomes after bilateral lung volume reduction surgery: prediction by quantitative CT. Chest 2001;119:1337–1346. - PubMed
-
- Geddes D, Davies M, Koyama H, Hansell D, Pastorino U, Pepper J, Agent P, Cullinan P, MacNeill SJ, Goldstraw P. Effect of lung-volume-reduction surgery in patients with severe emphysema. N Engl J Med 2000;343:239–245. - PubMed
-
- Sciurba FC, Rogers RM, Keenan RJ, Slivka WA, Gorcsan J 3rd, Ferson PF, Holbert JM, Brown ML, Landreneau RJ. Improvement in pulmonary function and elastic recoil after lung-reduction surgery for diffuse emphysema. N Engl J Med 1996;334:1095–1099. - PubMed
-
- Gelb AF, McKenna RJ Jr, Brenner M, Schein MJ, Zamel N, Fischel R. Lung function 4 years after lung volume reduction surgery for emphysema. Chest 1999;116:1608–1615. - PubMed
-
- Pompeo E, Marino M, Nofroni I, Matteucci G, Mineo TC. Reduction pneumoplasty versus respiratory rehabilitation in severe emphysema: a randomized study. Pulmonary Emphysema Research Group. Ann Thorac Surg 2000;70:948–953. [Discussion, 954.] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01HR76113/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76107/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76102/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76104/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76118/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76115/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76105/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76111/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76114/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76103/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76110/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76119/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76108/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76106/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76109/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76116/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76112/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HR76101/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
