COX-2/EGFR expression and survival among women with adenocarcinoma of the lung
- PMID: 18453539
- PMCID: PMC2527644
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgn107
COX-2/EGFR expression and survival among women with adenocarcinoma of the lung
Abstract
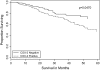
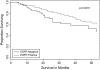
Previous studies suggest that cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression may predict survival among patients with non-small cell lung cancer. COX-2 may interact with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), suggesting that combined COX-2/EGFR expression may provide predictive value. The extent to which their independent or combined expression is associated with prognosis in women with adenocarcinoma of the lung is unknown. In the present study, we examined relationships between COX-2 expression (n = 238), EGFR expression (n = 158) and dual COX-2/EGFR expression (n = 157) and survival among women with adenocarcinoma of the lung. Overall survival was estimated by constructing Cox proportional hazards models adjusting for other significant variables and stratifying by stage at diagnosis and race. Clinical or demographic parameters were not associated with either COX-2 or EGFR expression. Patients with COX-2-positive tumors tended to have poorer prognosis than did patients with COX-2-negative tumors [hazard ratio (HR) 1.67, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.01-2.78]. African-Americans with COX-2-positive tumors had a statistically non-significant higher risk of death than African-Americans with COX-2-negative tumors (HR 5.58, 95% CI 0.64-48.37). No association between COX-2 expression and survival was observed among Caucasians (HR 1.29, 95% CI 0.72-2.30). EGFR expression was associated with a 44% reduction in the risk of death (HR 0.56, 95% CI 0.32-0.98). COX-2-/EGFR+ tumor expression, but not COX-2+/EGFR+ tumor expression, was associated with survival when compared with other combined expression results. In conclusion, COX-2 and EGFR expression, but not combined COX-2+/EGFR+ expression, independently predict survival of women with adenocarcinoma of the lung.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Monitoring of cyclooxygenase-2 levels can predict EGFR mutations and the efficacy of EGFR-TKI in patients with lung adenocarcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 May 1;8(5):5577-83. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26191267 Free PMC article.
-
Frequent co-localization of Cox-2 and laminin-5 gamma2 chain at the invasive front of early-stage lung adenocarcinomas.Am J Pathol. 2002 Mar;160(3):1129-41. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64933-4. Am J Pathol. 2002. PMID: 11891209 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarker analyses and final overall survival results from a phase III, randomized, open-label, first-line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer in Asia (IPASS).J Clin Oncol. 2011 Jul 20;29(21):2866-74. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.4235. Epub 2011 Jun 13. J Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21670455 Clinical Trial.
-
Relationship of tumor PD-L1 expression with EGFR wild-type status and poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2016 Oct;46(10):935-941. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyw087. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27511990
-
Has Cox-2 a prognostic role in non-small-cell lung cancer? A systematic review of the literature with meta-analysis of the survival results.Br J Cancer. 2006 Jul 17;95(2):139-45. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603226. Epub 2006 Jun 20. Br J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16786043 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pooled analysis of the clinical benefit of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors combined with chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2019 Aug;8(4):1258-1267. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.07.06. Transl Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 35116868 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in colorectal carcinoma, adenomatous polyps and non-tumour bearing margins of resection tissues in a cohort of black Africans.PLoS One. 2021 Jul 27;16(7):e0255235. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255235. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34314467 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2 is associated with malignant phenotypes in human lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2016 Nov;12(5):3836-3844. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5207. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27895738 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Expression of the EGF System-a Prognostic Model in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Without Activating EGFR Mutations.Transl Oncol. 2016 Aug;9(4):306-12. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2016.05.002. Transl Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27567953 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of cellular retinol binding protein-1 in lung adenocarcinoma is associated with poor prognosis.Genes Cancer. 2015 Nov;6(11-12):490-502. doi: 10.18632/genesandcancer.89. Genes Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26807202 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ries L, Melbert D, Krapcho M, Mariotto A, Miller BA, Feuer EJ, Clegg L, Horner MJ, Howlader N, Eisner MP, Reichman M, Edwards BK. 2007.
-
- Reckamp KL, et al. A phase I trial to determine the optimal biological dose of celecoxib when combined with erlotinib in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006;12:3381–3388. - PubMed
-
- O'Byrne KJ, et al. Combination therapy with gefitinib and rofecoxib in patients with platinum-pretreated relapsed non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007;25:3266–3273. - PubMed
-
- Gadgeel SM, et al. Phase II study of gefitinib, an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI), and celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor, in patients with platinum refractory non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) J. Thorac. Oncol. 2007;2:299–305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

