Stage-specific disruption of Stat3 demonstrates a direct requirement during both the initiation and promotion stages of mouse skin tumorigenesis
- PMID: 18453544
- PMCID: PMC2902397
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgn061
Stage-specific disruption of Stat3 demonstrates a direct requirement during both the initiation and promotion stages of mouse skin tumorigenesis
Abstract
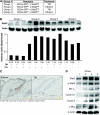
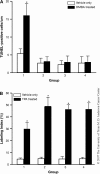
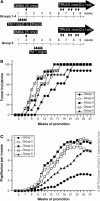
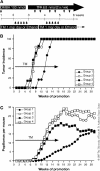
Constitutive activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) has been found in a variety of human malignancies and has been suggested to play an important role in carcinogenesis. Recently, our laboratory demonstrated that Stat3 is required for the development of skin tumors via two-stage carcinogenesis using skin-specific loss-of-function transgenic mice. To investigate further the role of Stat3 in each stage of chemical carcinogenesis in mouse skin, i.e. initiation and promotion stages, we generated inducible Stat3-deficient mice (K5.Cre-ER(T2) x Stat3(fl/fl)) that show epidermal-specific disruption of Stat3 following topical treatment with 4-hydroxytamoxifen (TM). The epidermis of inducible Stat3-deficient mice treated with TM showed a significant increase in apoptosis induced by 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA) and reduced proliferation following exposure to 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. In two-stage skin carcinogenesis assays, inducible Stat3-deficient mice treated with TM during the promotion stage showed a significant delay of tumor development and a significantly reduced number of tumors compared with control groups. Inducible Stat3-deficient mice treated with TM before initiation with DMBA also showed a significant delay in tumor development and a significantly reduced number of tumors compared with control groups. Finally, treatment of inducible Stat3-deficient mice that had existing skin tumors generated by the two-stage carcinogenesis protocol with TM (by intraperitoneal injection) led to inhibition of tumor growth compared with tumors formed in control groups. Collectively, these results directly demonstrate that Stat3 is required for skin tumor development during both the initiation and promotion stages of skin carcinogenesis in vivo.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

