Preferential costimulation by CD80 results in IL-10-dependent TGF-beta1(+) -adaptive regulatory T cell generation
- PMID: 18453575
- PMCID: PMC2435403
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.10.6566
Preferential costimulation by CD80 results in IL-10-dependent TGF-beta1(+) -adaptive regulatory T cell generation
Abstract
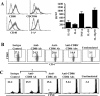
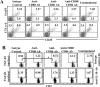
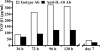
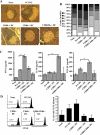
Costimulatory ligands CD80 and CD86 have different binding preferences and affinities to their receptors, CD28 and CTLA-4. Earlier, we demonstrated that CD80 binds to CTLA-4 with higher affinity and has a role in suppressing T cell response. The current study demonstrates that not only did blockade of CD86 upon Ag presentation by bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (DC) to OVA-specific T cells result in induction of hyporesponsive T cells but also that these T cells could suppress the proliferative response of effector T cells. These T cells showed TGF-beta1 on their surface and secreted TGF-beta1 and IL-10 upon restimulation. Although blockade of CTLA-4 and neutralization of IL-10 profoundly inhibited the induction of these TGF-beta1(+) T cells, their ability to suppress the effector T cell proliferation was abrogated by neutralization of TGF-beta1 alone. Induction of TGF-beta1(+) and IL-10(+) T cells was found to be independent of natural CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells, demonstrating that preferential ligation of CTLA-4 by CD80 induced IL-10 production by effector T cells, which in turn promoted the secretion of TGF-beta1. Treatment of prediabetic NOD mice with islet beta cell Ag-pulsed CD86(-/-) DCs, but not CD80(-/-) DCs, resulted in the induction of TGF-beta1- and IL-10-producing cells, significant suppression of insulitis, and delay of the onset of hyperglycemia. These observations demonstrate not only that CD80 preferentially binds to CTLA-4 but also that interaction during Ag presentation can result in IL-10-dependent TGF-beta1(+) regulatory T cell induction, reinstating the potential of approaches to preferentially engage CTLA-4 through CD80 during self-Ag presentation in suppressing autoimmunity.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Dendritic cell-directed CTLA-4 engagement during pancreatic beta cell antigen presentation delays type 1 diabetes.J Immunol. 2010 Jun 15;184(12):6695-708. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903130. Epub 2010 May 14. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20483724 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen-specific induced T regulatory cells impair dendritic cell function via an IL-10/MARCH1-dependent mechanism.J Immunol. 2013 Dec 15;191(12):5875-84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301693. Epub 2013 Nov 11. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24218453 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced engagement of CTLA-4 induces antigen-specific CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ and CD4+CD25- TGF-beta 1+ adaptive regulatory T cells.J Immunol. 2007 Oct 15;179(8):5191-203. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.8.5191. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17911604
-
Complexities of CD28/B7: CTLA-4 costimulatory pathways in autoimmunity and transplantation.Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:225-52. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.225. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11244036 Review.
-
The role of IL-10 and TGF-beta in the differentiation and effector function of T regulatory cells.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002 Dec;129(4):263-76. doi: 10.1159/000067596. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12483031 Review.
Cited by
-
Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells on Transplantation: Immunotherapy Based on Second Signal Blockage.J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:856707. doi: 10.1155/2015/856707. Epub 2015 Oct 12. J Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 26543876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
pH of drinking water influences the composition of gut microbiome and type 1 diabetes incidence.Diabetes. 2014 Feb;63(2):632-44. doi: 10.2337/db13-0981. Epub 2013 Nov 5. Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24194504 Free PMC article.
-
Role of dendritic cell maturity/costimulation for generation, homeostasis, and suppressive activity of regulatory T cells.Front Immunol. 2011 Sep 27;2:39. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2011.00039. eCollection 2011. Front Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22566829 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Autophagy Selective Therapeutics With Doxil: An Assessment of Pathological Toxicity.Front Toxicol. 2022 Jun 29;4:937150. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2022.937150. eCollection 2022. Front Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35846434 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of T cell checkpoint pathways during β-cell antigen presentation by engineered dendritic cells promotes protection from type 1 diabetes.Immunology. 2022 Jul;166(3):341-356. doi: 10.1111/imm.13476. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Immunology. 2022. PMID: 35404483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lenschow DJ, Walunas TL, Bluestone JA. CD28/B7 system of T cell costimulation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996;14:233–258. - PubMed
-
- Yi-qun Z, Lorre K, de Boer M, Ceuppens JL. B7-blocking agents, alone or in combination with cyclosporin A, induce antigen-specific anergy of human memory T cells. J. Immunol. 1997;158:4734–4740. - PubMed
-
- Walunas TL, Lenschow DJ, Bakker CY, Linsley PS, Freeman GJ, Green JM, Thompson CB, Bluestone JA. CTLA-4 can function as a negative regulator of T cell activation. Immunity. 1994;1:405–413. - PubMed
-
- Tivol EA, Borriello F, Schweitzer AN, Lynch WP, luestone JAB, Sharpe AH. Loss of CTLA-4 leads to massive lymphoproliferation and fatal multiorgan tissue destruction, revealing a critical negative regulatory role of CTLA-4. Immunity. 1995;3:541–547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

