DNA microarray gene expression profile of marginal zone versus follicular B cells and idiotype positive marginal zone B cells before and after immunization with Streptococcus pneumoniae
- PMID: 18453586
- PMCID: PMC3966313
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.10.6663
DNA microarray gene expression profile of marginal zone versus follicular B cells and idiotype positive marginal zone B cells before and after immunization with Streptococcus pneumoniae
Abstract
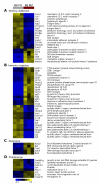
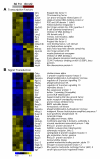
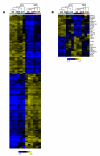
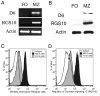
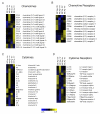
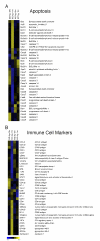
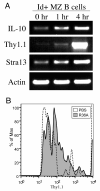
Marginal zone (MZ) B cells play an important role in the clearance of blood-borne bacterial infections via rapid T-independent IgM responses. We have previously demonstrated that MZ B cells respond rapidly and robustly to bacterial particulates. To determine the MZ-specific genes that are expressed to allow for this response, MZ and follicular (FO) B cells were sort purified and analyzed via DNA microarray analysis. We identified 181 genes that were significantly different between the two B cell populations. Ninety-nine genes were more highly expressed in MZ B cells while 82 genes were more highly expressed in FO B cells. To further understand the molecular mechanisms by which MZ B cells respond so rapidly to bacterial challenge, Id-positive and -negative MZ B cells were sort purified before (0 h) or after (1 h) i.v. immunization with heat-killed Streptococcus pneumoniae, R36A, and analyzed via DNA microarray analysis. We identified genes specifically up-regulated or down-regulated at 1 h following immunization in the Id-positive MZ B cells. These results give insight into the gene expression pattern in resting MZ vs FO B cells and the specific regulation of gene expression in Ag-specific MZ B cells following interaction with Ag.
Figures
References
-
- Martin F, Kearney JF. Marginal-zone B cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:323–335. - PubMed
-
- Dammers PM, Visser A, Popa ER, Nieuwenhuis P, Kroese FG. Most marginal zone B cells in rat express germline encoded Ig VH genes and are ligand selected. J Immunol. 2000;165:6156–6169. - PubMed
-
- Bendelac A, Bonneville M, Kearney JF. Autoreactivity by design: innate B and T lymphocytes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1:177–186. - PubMed
-
- Kearney JF. Innate-like B cells. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2005;26:377–383. - PubMed
-
- Oliver AM, Martin F, Gartland GL, Carter RH, Kearney JF. Marginal zone B cells exhibit unique activation, proliferative and immunoglobulin secretory responses. Eur J Immunol. 1997;27:2366–2374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

