Blockade of virus infection by human CD4+ T cells via a cytokine relay network
- PMID: 18453613
- PMCID: PMC2387070
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.10.6923
Blockade of virus infection by human CD4+ T cells via a cytokine relay network
Abstract
CD4(+) T cells directly participate in bacterial clearance through secretion of proinflammatory cytokines. Although viral clearance relies heavily on CD8(+) T cell functions, we sought to determine whether human CD4(+) T cells could also directly influence viral clearance through cytokine secretion. We found that IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha, secreted by IL-12-polarized Th1 cells, displayed potent antiviral effects against a variety of viruses. IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha acted directly to inhibit hepatitis C virus replication in an in vitro replicon system, and neutralization of both cytokines was required to block the antiviral activity that was secreted by Th1 cells. IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha also exerted antiviral effects against vesicular stomatitis virus infection, but in this case, functional type I IFN receptor activity was required. Thus, in cases of vesicular stomatitis virus infection, the combination of IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha secreted by human Th1 cells acted indirectly through the IFN-alpha/beta receptor. These results highlight the importance of CD4(+) T cells in directly regulating antiviral responses through proinflammatory cytokines acting in both a direct and indirect manner.
Figures
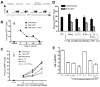
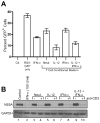
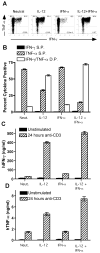
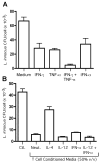
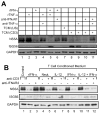
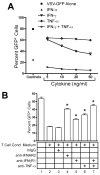
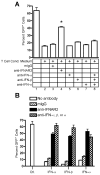
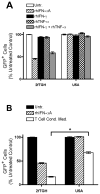
 ), rhTNF-α (◇), or rhIFN-γ + rhTNF-α (○) as indicated. (B) THP-1 cells were infected in the absence (1) or presence (–7) of 10% (v/v) T cell conditioned media from IL-12 + IFN-α activated T cells in the absence (2) or presence of 5 μg/ml mouse IgG1 isotype control antibody (3), 5 μg/ml anti-hIFNAR2 (4), 10 μg/ml anti-hIFNγR1 (5), 5 μg/ml anti-hTNF-α (6), or a combination of anti-hIFNγR1 and anti-hTNF-α (7).
), rhTNF-α (◇), or rhIFN-γ + rhTNF-α (○) as indicated. (B) THP-1 cells were infected in the absence (1) or presence (–7) of 10% (v/v) T cell conditioned media from IL-12 + IFN-α activated T cells in the absence (2) or presence of 5 μg/ml mouse IgG1 isotype control antibody (3), 5 μg/ml anti-hIFNAR2 (4), 10 μg/ml anti-hIFNγR1 (5), 5 μg/ml anti-hTNF-α (6), or a combination of anti-hIFNγR1 and anti-hTNF-α (7).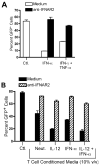
References
-
- Canessa A, Pistoia V, Roncella S, Merli A, Melioli G, Terragna A, Ferrarini M. An in vitro model for Toxoplasma infection in man: interaction between CD4+ monoclonal T cells and macrophages results in killing of trophozoites. J Immunol. 1988;140:3580–3588. - PubMed
-
- Geginat G, Lalic M, Kretschmar M, Goebel W, Hof H, Palm D, Bubert A. Th1 cells specific for a secreted protein of Listeria monocytogenes are protective in vivo. J Immunol. 1998;160:6046–6055. - PubMed
-
- Seder RA, Ahmed R. Similarities and differences in CD4+ and CD8+ effector and memory T cell generation. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:835–842. - PubMed
-
- Urbani S, Amadei B, Fisicaro P, Tola D, Orlandini A, Sacchelli L, Mori C, Missale G, Ferrari C. Outcome of acute hepatitis C is related to virus-specific CD4 function and maturation of antiviral memory CD8 responses. Hepatology. 2006;44:126–139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

