Spatial effects on the speed and reliability of protein-DNA search
- PMID: 18453629
- PMCID: PMC2441786
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn173
Spatial effects on the speed and reliability of protein-DNA search
Abstract
Strong experimental and theoretical evidence shows that transcription factors (TFs) and other specific DNA-binding proteins find their sites using a two-mode search: alternating between three-dimensional (3D) diffusion through the cell and one-dimensional (1D) sliding along the DNA. We show that, due to the 1D component of the search process, the search time of a TF can depend on the initial position of the TF. We formalize this effect by discriminating between two types of searches: global and local. Using analytical calculations and simulations, we estimate how close a TF and binding site need to be to make a local search likely. We then use our model to interpret the wide range of experimental measurements of this parameter. We also show that local and global searches differ significantly in average search time and the variability of search time. These results lead to a number of biological implications, including suggestions of how prokaryotes achieve rapid gene regulation and the relationship between the search mechanism and noise in gene expression. Lastly, we propose a number of experiments to verify the existence and quantify the extent of spatial effects on the TF search process in prokaryotes.
Figures
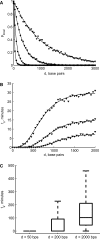
 = 10−6, 10−5, 10−4 and 10−3 M corresponding to se = 70 (circles), 210 (squares), 660 (diamonds), 2100 (triangles) bp, respectively. The solid line represents the analytical result and the markers represent the simulated result (ntrials = 1000/condition). (B) The average search time ts depends on several parameters—here we plot it as a function of d for several values of the copy number n = 5, 10 and 20 copies/cell;
= 10−6, 10−5, 10−4 and 10−3 M corresponding to se = 70 (circles), 210 (squares), 660 (diamonds), 2100 (triangles) bp, respectively. The solid line represents the analytical result and the markers represent the simulated result (ntrials = 1000/condition). (B) The average search time ts depends on several parameters—here we plot it as a function of d for several values of the copy number n = 5, 10 and 20 copies/cell;  = 10–5 M. As n increases, the probability of a local search increases and the global search time (the plateau) decreases. For small n, the difference in ts for small and large d is particularly striking. We simulated 5000 runs at each distance d. (C) The reliability of the search also depends on d. Here we plot the distribution of ts for d = 50, 200 and 2000 bp for a single TF. In the box and whisker plots, the box has lines at the lower quartile, median and upper quartile values. The whiskers extend from the box to 1.5 times the interquartile range, the difference between the lower and upper quartiles. Data points beyond the whiskers were excluded.
= 10–5 M. As n increases, the probability of a local search increases and the global search time (the plateau) decreases. For small n, the difference in ts for small and large d is particularly striking. We simulated 5000 runs at each distance d. (C) The reliability of the search also depends on d. Here we plot the distribution of ts for d = 50, 200 and 2000 bp for a single TF. In the box and whisker plots, the box has lines at the lower quartile, median and upper quartile values. The whiskers extend from the box to 1.5 times the interquartile range, the difference between the lower and upper quartiles. Data points beyond the whiskers were excluded.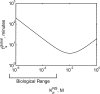
 . The search time is minimized when
. The search time is minimized when  is equal to the concentration of non-specific DNA, [D] = 10−2 M. However, the estimated range of
is equal to the concentration of non-specific DNA, [D] = 10−2 M. However, the estimated range of  is 10−6 to 10−3 M. See
is 10−6 to 10−3 M. See Similar articles
-
Modeling transcription factor binding events to DNA using a random walker/jumper representation on a 1D/2D lattice with different affinity sites.Phys Biol. 2007 Nov 21;4(4):256-67. doi: 10.1088/1478-3975/4/4/003. Phys Biol. 2007. PMID: 18185004
-
Asymmetric DNA-search dynamics by symmetric dimeric proteins.Biochemistry. 2013 Aug 13;52(32):5335-44. doi: 10.1021/bi400357m. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23866074
-
Generalized facilitated diffusion model for DNA-binding proteins with search and recognition states.Biophys J. 2012 May 16;102(10):2321-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.04.008. Epub 2012 May 15. Biophys J. 2012. PMID: 22677385 Free PMC article.
-
How motif environment influences transcription factor search dynamics: Finding a needle in a haystack.Bioessays. 2016 Jul;38(7):605-12. doi: 10.1002/bies.201600005. Epub 2016 May 19. Bioessays. 2016. PMID: 27192961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription Factors and DNA Play Hide and Seek.Trends Cell Biol. 2020 Jun;30(6):491-500. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2020.03.003. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Trends Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32413318 Review.
Cited by
-
Accelerated search kinetics mediated by redox reactions of DNA repair enzymes.Biophys J. 2009 May 20;96(10):3949-58. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.02.062. Biophys J. 2009. PMID: 19450467 Free PMC article.
-
How subdiffusion changes the kinetics of binding to a surface.Biophys J. 2009 Aug 5;97(3):710-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.05.022. Biophys J. 2009. PMID: 19651029 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive computational model of facilitated diffusion in prokaryotes.Bioinformatics. 2012 Jun 1;28(11):1517-24. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts178. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22492644 Free PMC article.
-
The bZIP dimer localizes at DNA full-sites where each basic region can alternately translocate and bind to subsites at the half-site.Biochemistry. 2012 Aug 21;51(33):6632-43. doi: 10.1021/bi300718f. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22856882 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo facilitated diffusion model.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53956. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053956. Epub 2013 Jan 18. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23349772 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Riggs AD, Bourgeois S, Cohn M. The lac repressor-operator interaction. 3. Kinetic studies. J. Mol. Biol. 1970;53:401–417. - PubMed
-
- Richter PH, Eigen M. Diffusion controlled reaction rates in spheroidal geometry. Application to repressor—operator association and membrane bound enzymes. Biophys. Chem. 1974;2:255–263. - PubMed
-
- Berg OG, Winter RB, von Hippel PH. Diffusion-driven mechanisms of protein translocation on nucleic acids. 1. Models and theory. Biochemistry. 1981;20:6929–6948. - PubMed
-
- Winter RB, Berg OG, von Hippel PH. Diffusion-driven mechanisms of protein translocation on nucleic acids. 3. The Escherichia coli lac repressor—operator interaction: kinetic measurements and conclusions. Biochemistry. 1981;20:6961–6977. - PubMed
-
- Shimamoto N. One-dimensional diffusion of proteins along DNA. Its biological and chemical significance revealed by single-molecule measurements. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:15293–15296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

