Structural and functional insights into human Tudor-SN, a key component linking RNA interference and editing
- PMID: 18453631
- PMCID: PMC2441809
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn236
Structural and functional insights into human Tudor-SN, a key component linking RNA interference and editing
Abstract
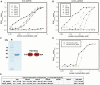
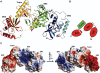
Human Tudor-SN is involved in the degradation of hyper-edited inosine-containing microRNA precursors, thus linking the pathways of RNA interference and editing. Tudor-SN contains four tandem repeats of staphylococcal nuclease-like domains (SN1-SN4) followed by a tudor and C-terminal SN domain (SN5). Here, we showed that Tudor-SN requires tandem repeats of SN domains for its RNA binding and cleavage activity. The crystal structure of a 64-kD truncated form of human Tudor-SN further shows that the four domains, SN3, SN4, tudor and SN5, assemble into a crescent-shaped structure. A concave basic surface formed jointly by SN3 and SN4 domains is likely involved in RNA binding, where citrate ions are bound at the putative RNase active sites. Additional modeling studies provide a structural basis for Tudor-SN's preference in cleaving RNA containing multiple I.U wobble-paired sequences. Collectively, these results suggest that tandem repeats of SN domains in Tudor-SN function as a clamp to capture RNA substrates.
Figures

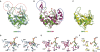


Similar articles
-
A micrococcal nuclease homologue in RNAi effector complexes.Nature. 2003 Sep 25;425(6956):411-4. doi: 10.1038/nature01956. Nature. 2003. PMID: 14508492
-
Tudor staphylococcal nuclease is a structure-specific ribonuclease that degrades RNA at unstructured regions during microRNA decay.RNA. 2018 May;24(5):739-748. doi: 10.1261/rna.064501.117. Epub 2018 Feb 13. RNA. 2018. PMID: 29440319 Free PMC article.
-
Tudor staphylococcal nuclease (Tudor-SN) participates in small ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) assembly via interacting with symmetrically dimethylated Sm proteins.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 25;287(22):18130-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.311852. Epub 2012 Apr 9. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22493508 Free PMC article.
-
Tudor staphylococcal nuclease: biochemistry and functions.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Nov 1;23(11):1739-1748. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.93. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 27612014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights Into SND1 Oncogene Promoter Regulation.Front Oncol. 2018 Dec 11;8:606. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00606. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30619748 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multifunction protein staphylococcal nuclease domain containing 1 (SND1) promotes tumor angiogenesis in human hepatocellular carcinoma through novel pathway that involves nuclear factor κB and miR-221.J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 20;287(17):13952-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.321646. Epub 2012 Mar 6. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22396537 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering arginine methylation: Tudor tells the tale.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Sep 14;12(10):629-42. doi: 10.1038/nrm3185. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21915143 Review.
-
Oncogenic Role of SND1 in Development and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancer Res. 2017 Jun 15;77(12):3306-3316. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0298. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28428278 Free PMC article.
-
Tudor-SN-mediated endonucleolytic decay of human cell microRNAs promotes G1/S phase transition.Science. 2017 May 26;356(6340):859-862. doi: 10.1126/science.aai9372. Science. 2017. PMID: 28546213 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcal nuclease and tudor domain-containing protein 1: An emerging therapeutic target in cancer (Review).Mol Clin Oncol. 2025 Jul 17;23(4):86. doi: 10.3892/mco.2025.2881. eCollection 2025 Oct. Mol Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40757241 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mello CC, Conte DJ. Revealing the world of RNA interference. Nature. 2004;431:338–342. - PubMed
-
- Broadhurst MK, Wheeler TT. The p100 coactivator is present in the nuclei of mammary epithelial cells and its abundance is increased in response to prolactin in culture and in mammary tissue during lactation. J. Endocrinol. 2001;171:329–337. - PubMed
-
- Zhao CT, Shi KH, Liang LY, Yan Y, Postlethwait J, Meng AM. Two variants of zebrafish p100 are expressed during embryogenesis and regulated by nodal signaling. FEBS Lett. 2003;543:190–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

