Magnetic resonance imaging-based finite element stress analysis after linear repair of left ventricular aneurysm
- PMID: 18455590
- PMCID: PMC3773224
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2007.11.038
Magnetic resonance imaging-based finite element stress analysis after linear repair of left ventricular aneurysm
Abstract
Objective: Linear repair of left ventricular aneurysm has been performed with mixed clinical results. By using finite element analysis, this study evaluated the effect of this procedure on end-systolic stress.
Methods: Nine sheep underwent myocardial infarction and aneurysm repair with a linear repair (13.4 +/- 2.3 weeks postmyocardial infarction). Satisfactory magnetic resonance imaging examinations were obtained in 6 sheep (6.6 +/- 0.5 weeks postrepair). Finite element models were constructed from in vivo magnetic resonance imaging-based cardiac geometry and postmortem measurement of myofiber helix angles using diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Material properties were iteratively determined by comparing the finite element model output with systolic tagged magnetic resonance imaging strain measurements.
Results: At the mid-wall, fiber stress in the border zone decreased by 39% (sham = 32.5 +/- 2.5 kPa, repair = 19.7 +/- 3.6 kPa, P = .001) to the level of remote regions after repair. In the septum, however, border zone fiber stress remained high (sham = 31.3 +/- 5.4 kPa, repair = 23.8 +/- 5.8 kPa, P = .29). Cross-fiber stress at the mid-wall decreased by 41% (sham = 13.0 +/- 1.5 kPa, repair = 7.7 +/- 2.1 kPa, P = .01), but cross-fiber stress in the un-excluded septal infarct was 75% higher in the border zone than remote regions (remote = 5.9 +/- 1.9 kPa, border zone = 10.3 +/- 3.6 kPa, P < .01). However, end-diastolic fiber and cross-fiber stress were not reduced in the remote myocardium after plication.
Conclusion: With the exception of the retained septal infarct, end-systolic stress is reduced in all areas of the left ventricle after infarct plication. Consequently, we expect the primary positive effect of infarct plication to be in the infarct border zone. However, the amount of stress reduction necessary to halt or reverse nonischemic infarct extension in the infarct border zone and eccentric hypertrophy in the remote myocardium is unknown.
Figures

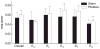
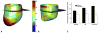

Similar articles
-
MRI-based finite-element analysis of left ventricular aneurysm.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005 Aug;289(2):H692-700. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01226.2004. Epub 2005 Mar 18. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15778283
-
The effect of anteroapical aneurysm plication on end-systolic three-dimensional strain in the sheep: a magnetic resonance imaging tagging study.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006 Mar;131(3):579-586.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2005.07.065. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006. PMID: 16515908 Free PMC article.
-
Helical myofiber orientation after myocardial infarction and left ventricular surgical restoration in sheep.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005 Feb;129(2):382-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2004.06.006. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005. PMID: 15678050
-
[Surgical treatment of pseudoaneurysm of the left ventricle after myocardial infarction--a case report].Nihon Kyobu Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1993 Jun;41(6):1040-4. Nihon Kyobu Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1993. PMID: 8336030 Review. Japanese.
-
Surgery for left ventricular aneurysm after myocardial infarction: techniques selection and results assessment.Chin Med J (Engl). 2012 Dec;125(24):4373-9. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012. PMID: 23253704 Review.
Cited by
-
Parameter estimation in a Holzapfel-Ogden law for healthy myocardium.J Eng Math. 2015;95(1):231-248. doi: 10.1007/s10665-014-9740-3. Epub 2015 Jan 30. J Eng Math. 2015. PMID: 26663931 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo estimation of passive biomechanical properties of human myocardium.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018 Sep;56(9):1615-1631. doi: 10.1007/s11517-017-1768-x. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018. PMID: 29479659 Free PMC article.
-
Fluid-Structure Interactions of the Mitral Valve and Left Heart: Comprehensive Strategies, Past, Present and Future.Int J Numer Methods Eng. 2010 Mar;26(3-4):348-380. doi: 10.1002/cnm.1280. Int J Numer Methods Eng. 2010. PMID: 20454531 Free PMC article.
-
First finite element model of the left ventricle with mitral valve: insights into ischemic mitral regurgitation.Ann Thorac Surg. 2010 May;89(5):1546-53. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2010.02.036. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010. PMID: 20417775 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of surgical ventricular restoration on ventricular shape, wall stress, and function in heart failure patients.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 May;300(5):H1653-60. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00021.2011. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21357513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cooley D, Collins H, Morris G, Chapman D. Ventricular aneurysm after myocardial infarction: surgical excision with use of temporary cardio-pulmonary bypass. JAMA. 1958;167:557. - PubMed
-
- Taniguchi K, Sakurai M, Takahashi T, Imagawa H, Mitsuno M, Nakano S, et al. Postinfarction left-ventricular aneurysm: regional stress, function, and remodeling after aneurysmectomy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1998;46:253–9. - PubMed
-
- Kramer CM, Magovern JA, Rogers WJ, Vido D, Savage EB. Reverse remodeling and improved regional function after repair of left ventricular aneurysm. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002;123:700–6. - PubMed
-
- Versteegh MI, Lamb HJ, Bax JJ, Curiel FB, van der Wall EE, de Roos A, et al. MRI evaluation of left ventricular function in anterior LV aneurysms before and after surgical resection. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2003;23:609–13. - PubMed
-
- Ratcliffe MB, Wallace AW, Salahieh A, Hong J, Ruch S, Hall TS. Ventricular volume, chamber stiffness, and function after anteroapical aneurysm plication in the sheep. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000;119:115–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

