Cystatin C and creatinine in an HIV cohort: the nutrition for healthy living study
- PMID: 18455851
- PMCID: PMC4430838
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.01.027
Cystatin C and creatinine in an HIV cohort: the nutrition for healthy living study
Abstract
Background: Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected persons have an increased risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Serum creatinine level may underestimate the prevalence of CKD in subjects with decreased lean body mass or liver disease. Level of serum cystatin C, an alternative kidney function marker, is independent of lean body mass.
Study design: Cross-sectional.
Setting & participants: 250 HIV-infected subjects on highly active antiretroviral therapy in the Nutrition for Healthy Living (NFHL) cohort; 2,628 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2001-2002 subjects.
Predictors & outcomes: Comparison of serum creatinine levels in NFHL to those in NHANES subjects; comparison of CKD in NFHL subjects ascertained using serum creatinine versus cystatin C levels.
Measurements: Standardized serum creatinine, serum cystatin C, glomerular filtration rate (GFR) estimated from serum creatinine and cystatin C levels.
Results: Creatinine levels were lower in NFHL than NHANES subjects despite greater rates of hepatitis, diabetes, and drug use (mean difference, -0.18 mg/dL; P < 0.001 adjusted for age, sex, and race). Of NFHL subjects, only 2.4% had a creatinine-based estimated GFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m(2), but 15.2% had a cystatin-based estimated GFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m(2).
Limitations: GFR was estimated rather than measured. Other factors in addition to GFR may affect creatinine and cystatin C levels. Measurements of proteinuria were not available.
Conclusions: Serum creatinine levels may overestimate GFRs in HIV-infected subjects. Kidney disease prevalence may be greater than previously appreciated.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential Conflicts of Interest:
Clara Y. Jones, MD: None
Camille A. Jones, MD: None
Ira B. Wilson, MD: None
Tamsin A. Knox, MD: None
Andrew S. Levey, MD: None
Donna Spiegelman, PhD: None
Sherwood L.Gorbach, MD: None
Frederick Van Lente, PhD: None
Lesley A. Stevens, MD: None
Figures
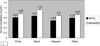
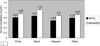
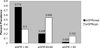
Similar articles
-
Differential estimation of CKD using creatinine- versus cystatin C-based estimating equations by category of body mass index.Am J Kidney Dis. 2009 Jun;53(6):993-1001. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.12.043. Epub 2009 Apr 25. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009. PMID: 19394726 Free PMC article.
-
Cystatin C level as a marker of kidney function in human immunodeficiency virus infection: the FRAM study.Arch Intern Med. 2007 Nov 12;167(20):2213-9. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.20.2213. Arch Intern Med. 2007. PMID: 17998494 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating GFR using serum cystatin C alone and in combination with serum creatinine: a pooled analysis of 3,418 individuals with CKD.Am J Kidney Dis. 2008 Mar;51(3):395-406. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2007.11.018. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008. PMID: 18295055 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding estimated glomerular filtration rate: implications for identifying chronic kidney disease.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2007 May;16(3):242-9. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e328057de8b. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2007. PMID: 17420668 Review.
-
How to use… serum creatinine, cystatin C and GFR.Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed. 2017 Feb;102(1):37-43. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2016-311062. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed. 2017. PMID: 27647862 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of risk factors and outcomes in HIV immune complex kidney disease and HIV-associated nephropathy.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013 Sep;8(9):1524-32. doi: 10.2215/CJN.10991012. Epub 2013 May 16. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23685946 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparison of Creatinine, Cystatin C, and Creatinine-Cystatin C Based Equations in HIV/AIDS Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study.Health Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 12;7(12):e70263. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70263. eCollection 2024 Dec. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39669187 Free PMC article.
-
Cystatin C-Based Evaluation of Kidney Function of HIV-Infected Children in Benin City, Southern Nigeria.Int J Nephrol. 2012;2012:861296. doi: 10.1155/2012/861296. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Int J Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 23213527 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence of renal impairment in individuals seeking HIV testing in Urban Malawi.BMC Nephrol. 2016 Nov 22;17(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s12882-016-0403-7. BMC Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27875991 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in estimation of creatinine generation between renal function estimating equations in an Indian population: cross-sectional data from the Hyderabad arm of the Indian migration study.BMC Nephrol. 2013 Feb 4;14:30. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-14-30. BMC Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23379609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amin J, Kaye M, Skidmore S, Pillay D, Cooper D, Dore G. HIV and Hepatitis C Coinfection Within The CAESAR Study. HIV Medicine. 2004;5:174–179. - PubMed
-
- Strader D. Coinfection with HIV and Hepatitis C virus in Injection Drug Users and Minority Populations. Clinical Infectious Disease. 2005;41:S7–S13. - PubMed
-
- DiGiambenedetto S, Baldini F, Cingolani A, Tamburrini E, Cauda R, DeLuca A. The Influence of Hepatitis C Virus Coinfection on the Risk of Lipid Abnormalities in a Cohort of HIV-1-Infected Patients After Initiation of Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy. JAIDS. 2004;36:641–642. - PubMed
-
- Schneider E, Glynn M, Kajese T, McKenna M. Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS - United States, 1981–2005. MMWR. 2006;55:589–590. - PubMed
-
- Conaldi P, Biancone L, Bottelli A, Wade-Evans A, Racusen L, Boccellino M, Orlandi V, Serra C, Camussi G, Toniolo A. HIV-1 Kills Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells in vitro by Triggering an Apoptotic Pathway Involving Caspase Activation and Fas Upregulation. J Clin Invest. 1998;102:2041–2049. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

