A dynamic pathway for calcium-independent activation of CaMKII by methionine oxidation
- PMID: 18455987
- PMCID: PMC2435269
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.048
A dynamic pathway for calcium-independent activation of CaMKII by methionine oxidation
Abstract
Calcium/calmodulin (Ca2+/CaM)-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) couples increases in cellular Ca2+ to fundamental responses in excitable cells. CaMKII was identified over 20 years ago by activation dependence on Ca2+/CaM, but recent evidence shows that CaMKII activity is also enhanced by pro-oxidant conditions. Here we show that oxidation of paired regulatory domain methionine residues sustains CaMKII activity in the absence of Ca2+/CaM. CaMKII is activated by angiotensin II (AngII)-induced oxidation, leading to apoptosis in cardiomyocytes both in vitro and in vivo. CaMKII oxidation is reversed by methionine sulfoxide reductase A (MsrA), and MsrA-/- mice show exaggerated CaMKII oxidation and myocardial apoptosis, impaired cardiac function, and increased mortality after myocardial infarction. Our data demonstrate a dynamic mechanism for CaMKII activation by oxidation and highlight the critical importance of oxidation-dependent CaMKII activation to AngII and ischemic myocardial apoptosis.
Figures

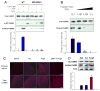
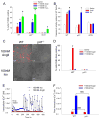
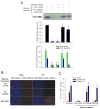
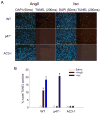
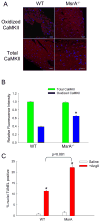
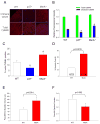
Comment in
-
CaMKII: new tricks for an old dog.Cell. 2008 May 2;133(3):397-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.04.018. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18455979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Effect of metoprolol CR/XL in chronic heart failure: Metoprolol CR/XL Randomized Intervention Trial in Congestive Heart Failure (MERIT-HF) Lancet. 1999;353:2001–2007. - PubMed
-
- Barford D. The role of cysteine residues as redox-sensitive regulatory switches. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004;14:679–686. - PubMed
-
- Bers DM. Beyond beta blockers. Nat Med. 2005;11:379–380. - PubMed
-
- Colbran RJ. Inactivation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II by basal autophosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:7163–7170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL079031/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL084583/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RR017369/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH063232/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM057001/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL 62494/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K26 RR017369/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL062494/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL 079031/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL083422/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM57001/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL 70250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

