Identification of positionally distinct astrocyte subtypes whose identities are specified by a homeodomain code
- PMID: 18455991
- PMCID: PMC2394859
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.046
Identification of positionally distinct astrocyte subtypes whose identities are specified by a homeodomain code
Abstract
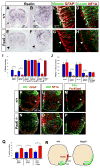
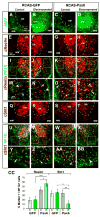
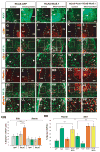
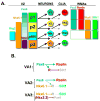
Astrocytes constitute the most abundant cell type in the central nervous system (CNS) and play diverse functional roles, but the ontogenetic origins of this phenotypic diversity are poorly understood. We have investigated whether positional identity, a fundamental organizing principle governing the generation of neuronal subtype diversity, is also relevant to astrocyte diversification. We identified three positionally distinct subtypes of white-matter astrocytes (WMA) in the spinal cord, which can be distinguished by the combinatorial expression of Reelin and Slit1. These astrocyte subtypes derive from progenitor domains expressing the homeodomain transcription factors Pax6 and Nkx6.1, respectively. Loss- and gain-of-function experiments indicate that the positional identity of these astrocyte subtypes is controlled by Pax6 and Nkx6.1 in a combinatorial manner. Thus, positional identity is an organizing principle underlying astrocyte, as well as neuronal, subtype diversification and is controlled by a homeodomain transcriptional code whose elements are reutilized following the specification of neuronal identity earlier in development.
Figures



References
-
- Bailey MS, Shipley MT. Astrocyte subtypes in the rat olfactory bulb: Morphological heterogeneity and differential laminar distribution. The Journal of comparative neurology. 1993;328:501–526. - PubMed
-
- Briscoe J, Ericson J. Specification of neuronal fates in the ventral neural tube. Current opinion in neurobiology. 2001;11:43–49. - PubMed
-
- Briscoe J, Pierani A, Jessell TM, Ericson J. A Homeodomain Protein Code Specifies Progenitor Cell Identity and Neuronal Fate in the Ventral Neural Tube. Cell. 2000;101:435–445. - PubMed
-
- Briscoe J, Sussel L, Serup P, Hartigan-O’Connor D, Jessell TM, Rubenstein JL, Ericson J. Homeobox gene Nkx2.2 and specification of neuronal identity by graded Sonic hedgehog signalling. Nature. 1999;398:622–627. - PubMed
-
- Brose K, Bland KS, Wang KH, Arnott D, Henzel W, Goodman CS, Tessier-Lavigne M, Kidd T. Slit proteins bind Robo receptors and have an evolutionarily conserved role in repulsive axon guidance. Cell. 1999;96:795–806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

