Effect of drug-paired exteroceptive stimulus presentations on methamphetamine reinstatement in rats
- PMID: 18456312
- PMCID: PMC3878429
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2008.03.028
Effect of drug-paired exteroceptive stimulus presentations on methamphetamine reinstatement in rats
Abstract
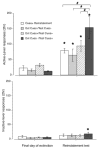
The purpose of the present study was to examine the impact of drug-paired cues on methamphetamine reinstatement. Three groups of rats were trained to self-administer 0.1 mg/kg/infusion methamphetamine. Each methamphetamine infusion was accompanied by a 6 s flashing light+tone stimulus (cues). After training, the groups were then given 12, daily extinction sessions either with or without response-contingent drug-paired cues and then tested for 1 mg/kg i.p. methamphetamine priming-induced reinstatement either with or without cues. Methamphetamine priming significantly reinstated drug-appropriate responding regardless of whether response-contingent cues were omitted during both extinction and testing, presented during both extinction and testing, or omitted during extinction but presented during reinstatement testing. The group in which cues were omitted during extinction and presented during reinstatement exhibited significantly greater reinstatement than did the other two groups. A separate group of rats was also tested demonstrating that response-contingent presentation of previously methamphetamine-paired cues alone, without methamphetamine priming, significantly reinstated drug-appropriate responding. These data show that methamphetamine priming produces a robust reinstatement effect which can be influenced by drug-paired cues.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmed SH, Walker JR, Koob GF. Persistent increase in the motivation to take heroin in rats with a history of drug escalation. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2000;22:413–21. - PubMed
-
- Alleweireldt AT, Weber SM, Kirschner KF, Bullock BL, Neisewander JL. Blockade or stimulation of D1 dopamine receptors attenuates cue reinstatement of extinguished cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2002;159:284–93. - PubMed
-
- Anggadiredja K, Nakamichi M, Hiranita T, Tanaka H, Shoyama Y, Watanabe S, Yamamoto T. Endocannabinoid system modulates relapse to methamphetamine seeking: possible mediation by the arachidonic acid cascade. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004a;29:1470–8. - PubMed
-
- Anggadiredja K, Sakimura K, Hiranita T, Yamamoto T. Naltrexone attenuates cue- but not drug-induced methamphetamine seeking: a possible mechanism for the dissociation of primary and secondary reward. Brain Res. 2004b;1021:272–6. - PubMed
-
- Caggiula AR, Donny EC, White AR, Chaudhri N, Booth S, Gharib MA, Hoffman A, Perkins KA, Sved AF. Environmental stimuli promote the acquisition of nicotine self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2002;163:230–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

