Virus-specific intestinal IFN-gamma producing T cell responses induced by human rotavirus infection and vaccines are correlated with protection against rotavirus diarrhea in gnotobiotic pigs
- PMID: 18456375
- PMCID: PMC2574896
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.03.085
Virus-specific intestinal IFN-gamma producing T cell responses induced by human rotavirus infection and vaccines are correlated with protection against rotavirus diarrhea in gnotobiotic pigs
Abstract
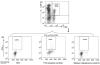
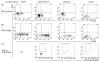
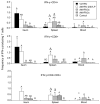
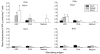
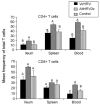
We examined rotavirus-specific IFN-gamma producing CD4+, CD8+ and CD4+CD8+ T cell responses in gnotobiotic pigs infected with a virulent human rotavirus (VirHRV) or vaccinated with an attenuated (Att) HRV vaccine (AttHRV3x or AttHRV2x) or an AttHRV oral priming and 2/6-virus-like particle (VLP) intranasal boosting (AttHRV-2/6VLP) regimen. In VirHRV infected pigs, HRV-specific IFN-gamma producing T cells reside primarily in ileum. AttHRV-2/6VLP induced similar frequencies of intestinal IFN-gamma producing T cells as the VirHRV, whereas AttHRV3x or 2x vaccines were less effective. Protection rates against rotavirus diarrhea upon VirHRV challenge significantly correlated (r=0.97-1.0, p<0.005) with frequencies of intestinal IFN-gamma producing T cells, suggesting their role in protective immunity.
Figures

References
-
- Iosef C, Van Nguyen T, Jeong K, Bengtsson K, Morein B, Kim Y, et al. Systemic and intestinal antibody secreting cell responses and protection in gnotobiotic pigs immunized orally with attenuated Wa human rotavirus and Wa 2/6-rotavirus-like-particles associated with immunostimulating complexes. Vaccine. 2002;20(13–14):1741–53. - PubMed
-
- Yuan L, Iosef C, Azevedo MS, Kim Y, Qian Y, Geyer A, et al. Protective immunity and antibody-secreting cell responses elicited by combined oral attenuated Wa human rotavirus and intranasal Wa 2/6-VLPs with mutant Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin in gnotobiotic pigs. J Virol. 2001;75(19):9229–38. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

