The modulation of voltage-gated potassium channels by anisotonicity in trigeminal ganglion neurons
- PMID: 18456412
- PMCID: PMC2517136
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.03.046
The modulation of voltage-gated potassium channels by anisotonicity in trigeminal ganglion neurons
Abstract
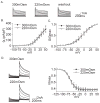
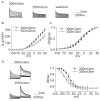
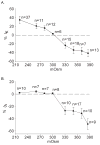
Voltage-gated potassium channels (VGPCs) play an important role in many physiological functions by controlling the electrical properties and excitability of cells. Changes in tonicity in the peripheral nervous system can activate nociceptors and produce pain. Here, using whole cell patch clamp techniques, we explore how hypo- and hypertonicity modulate VGPCs in cultured rat and mouse trigeminal ganglion (TG) neurons. We found that hypo- and hypertonicity had different effects on slow-inactivating K+ current (IK) and fast-inactivating K+ current (IA): hypotonicity increased IK but had no effect on IA while hypertonicity depressed both IK and IA. The increase of IK by hypotonicity was mimicked by transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) receptor activator 4alpha-phorbol-12,13-didecanoate (4alpha-PDD) but hypotonicity did not exhibit increase in TRPV4-/- mice TG neurons, suggesting that TRPV4 receptor was involved in hypotonicity-induced response. We also found that inactivation of PKC selectively reversed the increase of IK by hypotonicity, whereas antagonism of G-protein selectively rescued the inhibitions of IK and IA by hypertonicity, indicating that different intracellular signaling pathways were required for the modulation by hypo- and hypertonicity. In summary, changes in osmolality have various effects on IK and IA and different receptors and second messenger systems are selective for the modulation of VGPCs induced by hypo- versus hypertonicity.
Figures


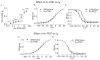
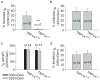
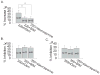
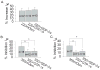

Similar articles
-
Changes in osmolality modulate voltage-gated sodium channels in trigeminal ganglion neurons.Neurosci Res. 2009 Jun;64(2):199-207. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2009.02.012. Epub 2009 Mar 13. Neurosci Res. 2009. PMID: 19428701 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in osmolality modulate voltage-gated calcium channels in trigeminal ganglion neurons.Brain Res. 2008 May 7;1208:56-66. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.02.048. Epub 2008 Feb 29. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18378217 Free PMC article.
-
Osmolality-induced tuning of action potentials in trigeminal ganglion neurons.Neurosci Lett. 2009 Mar 6;452(1):79-83. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.01.022. Neurosci Lett. 2009. PMID: 19444958 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effects of capsaicin on voltage-gated potassium channels by TRPV1-independent pathway.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2014 May;34(4):565-76. doi: 10.1007/s10571-014-0041-1. Epub 2014 Mar 4. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24590823 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in osmolality sensitize the response to capsaicin in trigeminal sensory neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2007 Mar;97(3):2001-15. doi: 10.1152/jn.00887.2006. J Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17353553
Cited by
-
Principal neuron diversity in the murine lateral superior olive supports multiple sound localization strategies and segregation of information in higher processing centers.Commun Biol. 2023 Apr 19;6(1):432. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04802-5. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37076594 Free PMC article.
-
A QUARTER CENTURY OF CALCIUM-PERMEABLE ION CHANNEL, TRPV4: PERSPECTIVES ON EXPRESSION AND FUNCTION IN ENDOTHELIAL CELLS-TIME TO TRANSLATE.Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2025;135:240-259. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2025. PMID: 40771603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 Increases NMDA-Activated Current in Hippocampal Pyramidal Neurons.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Mar 4;7:17. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00017. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23459987 Free PMC article.
-
Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 Inhibits γ-Aminobutyric Acid-Activated Current in Hippocampal Pyramidal Neurons.Front Mol Neurosci. 2016 Aug 26;9:77. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00077. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27616980 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting TRP channels for novel migraine therapeutics.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014 Nov 19;5(11):1085-96. doi: 10.1021/cn500083e. Epub 2014 Aug 29. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25138211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akins PT, McCleskey EW. Characterization of potassium currents in adult rat sensory neurons and modulation by opioids and cyclic AMP. Neuroscience. 1993;56:759–769. - PubMed
-
- Alessandri-Haber N, Joseph E, Dina OA, Liedtke W, Levine JD. TRPV4 mediates pain-related behavior induced by mild hypertonic stimuli in the presence of inflammatory mediator. Pain. 2005;118:70–79. - PubMed
-
- Alessandri-Haber N, Yeh JJ, Boyd AE, Parada CA, Chen X, Reichling DB, Levine JD. Hypotonicity induces TRPV4-mediated nociception in rat. Neuron. 2003;39:497–511. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

