High-dose interleukin-2 for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma : a retrospective analysis of response and survival in patients treated in the surgery branch at the National Cancer Institute between 1986 and 2006
- PMID: 18457330
- PMCID: PMC3486432
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.23552
High-dose interleukin-2 for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma : a retrospective analysis of response and survival in patients treated in the surgery branch at the National Cancer Institute between 1986 and 2006
Abstract
Background: The treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with high-dose interleukin-2 (HD IL-2) has resulted in durable tumor regression in a minority of patients. The current study presents the authors' 20-year experience administering this immunotherapeutic agent.
Methods: Patients with metastatic RCC (n = 259) were treated with HD IL-2 alone from January 13, 1986 through December 31, 2006 at the Surgery Branch of the National Cancer Institute. Potential predictive factors for response and survival, both pretreatment and treatment-related, were first subjected to univariate analysis and then to multivariate logistic regression or a Cox proportional hazards model. Finally, the authors investigated Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) prognostic factors for survival to assess their predictive value in the patient population in the current study.
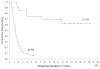
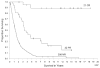
Results: A total of 23 patients experienced a complete response and 30 patients achieved a partial response, for an overall objective response rate of 20%. All partial responders had developed disease recurrence at the time of last follow-up, but only 4 complete responders had experienced disease recurrence by that time. Despite toxicities, only 2 patients developed treatment-related mortalities over this same time period. A higher baseline weight (P = .05) and MSKCC prognostic factors (P = .02) were found to be the variables most associated with response. For survival >4 years and overall survival, several pretreatment and treatment-related factors maintained significance, but none more so than response (P < .0001).
Conclusions: HD IL-2 can induce complete tumor regression in a small number of patients, and many patients have experienced extended disease-free intervals. Given its relative safety, HD IL-2 should still be considered a first-line therapy in patients with metastatic RCC who have an overall good performance status.
Figures
References
-
- SEER Database. Cancer of the Kidney and Renal Pelvis. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program; 2007.
-
- Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, et al., editors. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 6. Chapter 36. New York: Springer; 2002. pp. 323–328.
-
- Yang JC, Topalian SL, Schwartzentruber DJ, et al. The use of polyethylene glycol-modified interleukin-2 (PEG-IL-2) in the treatment of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma and melanoma: a Phase I study and a randomized prospective study comparing IL-2 alone versus IL-2 combined with PEG-IL-2. Cancer. 1995;76:687–694. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT, Yang JC, et al. Combination therapy with interleukin-2 and alpha-interferon for the treatment of patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1989;7:1863–1874. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical