Inhibition of serine proteases by a new class of cyclosulfamide-based carbamylating agents
- PMID: 18457652
- PMCID: PMC2492831
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2008.04.020
Inhibition of serine proteases by a new class of cyclosulfamide-based carbamylating agents
Abstract
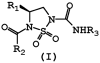
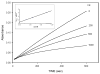
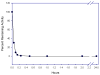
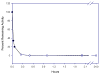
A new class of carbamylating agents based on the cyclosulfamide scaffold is reported. These compounds were found to be efficient time-dependent inhibitors of human neutrophil elastase (HNE). Exploitation of the three sites of diversity present in the cyclosulfamide scaffold yielded compounds which inhibited HNE but not proteinase 3 (PR 3) or bovine trypsin. The findings reported herein suggest that the introduction of appropriate recognition elements into the cyclosulfamide scaffold may lead to highly selective agents of potential value in the design of activity-based probes suitable for investigating proteases associated with the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, and in vitro evaluation of inhibitors of human leukocyte elastase based on a functionalized cyclic sulfamide scaffold.Bioorg Med Chem. 2004 Feb 1;12(3):589-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2003.10.059. Bioorg Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 14738969
-
Inactivation of human neutrophil elastase by 1,2,5-thiadiazolidin-3-one 1,1 dioxide-based sulfonamides.Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Jan 15;16(2):692-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2007.10.041. Epub 2007 Oct 18. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 17976994 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of serine proteases by functionalized sulfonamides coupled to the 1,2,5-thiadiazolidin-3-one 1,1 dioxide scaffold.Bioorg Med Chem. 2001 Jun;9(6):1543-8. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(01)00037-2. Bioorg Med Chem. 2001. PMID: 11408173
-
Natural compounds as inhibitors of human neutrophil elastase.Planta Med. 2007 May;73(5):401-20. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-967183. Epub 2007 Apr 20. Planta Med. 2007. PMID: 17447201 Review.
-
Beta-sultams-mechanism of reactions and use as inhibitors of serine proteases.Acc Chem Res. 2004 May;37(5):297-303. doi: 10.1021/ar0200899. Acc Chem Res. 2004. PMID: 15147170 Review.
Cited by
-
Neutrophil elastase inhibitors.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2011 Mar;21(3):339-54. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2011.551115. Epub 2011 Jan 16. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2011. PMID: 21235378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intramolecular 1,5-C(sp3)-H Radical Amination via Co(II)-Based Metalloradical Catalysis for Five-Membered Cyclic Sulfamides.Chem Sci. 2016;7(12):6934-6939. doi: 10.1039/C6SC02231F. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Chem Sci. 2016. PMID: 28138382 Free PMC article.
-
Catalytic asymmetric synthesis of cyclic sulfamides from conjugated dienes.Org Lett. 2013 Feb 15;15(4):796-9. doi: 10.1021/ol303469a. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Org Lett. 2013. PMID: 23362985 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

