Site-specific release of nascent chains from ribosomes at a sense codon
- PMID: 18458056
- PMCID: PMC2447138
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00421-08
Site-specific release of nascent chains from ribosomes at a sense codon
Abstract
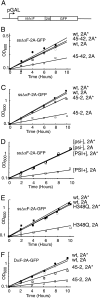
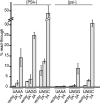
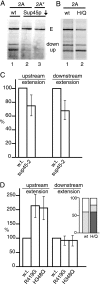
"2A" oligopeptides are autonomous elements containing a D(V/I)EXNPGP motif at the C terminus. Protein synthesis from an open reading frame containing an internal 2A coding sequence yields two separate polypeptides, corresponding to sequences up to and including 2A and those downstream. We show that the 2A reaction occurs in the ribosomal peptidyltransferase center. Ribosomes pause at the end of the 2A coding sequence, over the glycine and proline codons, and the nascent chain up to and including this glycine is released. Translation-terminating release factors eRF1 and eRF3 play key roles in the reaction. On the depletion of eRF1, a greater proportion of ribosomes extend through the 2A coding sequence, yielding the full-length protein. In contrast, impaired eRF3 GTPase activity leads to many ribosomes failing to translate beyond 2A. Further, high-level expression of a 2A peptide-containing protein inhibits the growth of cells compromised for release factor activity and leads to errors in stop codon recognition. We propose that the nascent 2A peptide interacts with ribosomes to drive a highly unusual and specific "termination" reaction, despite the presence of a proline codon in the A site. After this, the majority of ribosomes continue translation, generating the separate downstream product.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Orchestrating ribosomal activity from inside: effects of the nascent chain on the peptidyltransferase centre.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Dec;38(6):1576-80. doi: 10.1042/BST0381576. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 21118129 Review.
-
Misdecoding of rare CGA codon by translation termination factors, eRF1/eRF3, suggests novel class of ribosome rescue pathway in S. cerevisiae.FEBS J. 2019 Feb;286(4):788-802. doi: 10.1111/febs.14709. Epub 2018 Dec 11. FEBS J. 2019. PMID: 30471181 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of translation termination mediated by an interaction of eukaryotic release factor 1 with a nascent peptidyl-tRNA.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Dec;22(24):8562-70. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.24.8562-8570.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12446775 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic release factor 3 is required for multiple turnovers of peptide release catalysis by eukaryotic release factor 1.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 11;288(41):29530-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.487090. Epub 2013 Aug 20. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23963452 Free PMC article.
-
Structural aspects of translation termination on the ribosome.RNA. 2011 Aug;17(8):1409-21. doi: 10.1261/rna.2733411. Epub 2011 Jun 23. RNA. 2011. PMID: 21700725 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of CIDEA reporter mouse model and its application for screening thermogenic drugs.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 16;11(1):18429. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97959-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34531447 Free PMC article.
-
Please do not recycle! Translation reinitiation in microbes and higher eukaryotes.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2018 Mar 1;42(2):165-192. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fux059. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29281028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tandem termination signal in plant mRNAs.Gene. 2011 Jul 15;481(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2011.04.002. Epub 2011 Apr 22. Gene. 2011. PMID: 21539902 Free PMC article.
-
APE-type non-LTR retrotransposons of multicellular organisms encode virus-like 2A oligopeptide sequences, which mediate translational recoding during protein synthesis.Mol Biol Evol. 2013 Aug;30(8):1955-65. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst102. Epub 2013 May 31. Mol Biol Evol. 2013. PMID: 23728794 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic comparison of nonviral gene delivery strategies for efficient co-expression of two transgenes in human mesenchymal stem cells.J Biol Eng. 2023 Dec 7;17(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s13036-023-00394-0. J Biol Eng. 2023. PMID: 38062439 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkalaeva, E. Z., A. V. Pisarev, L. Y. Frolova, L. L. Kisselev, and T. V. Pestova. 2006. In vitro reconstitution of eukaryotic translation reveals cooperativity between release factors eRF1 and eRF3. Cell 1251125-1136. - PubMed
-
- Anthony, D. D., and W. C. Merrick. 1992. Analysis of 40 S and 80 S complexes with mRNA as measured by sucrose density gradients and primer extension inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2671554-1562. - PubMed
-
- Atkins, J. F., N. M. Wills, G. Loughran, C. Y. Wu, K. Parsawar, M. D. Ryan, C. H. Wang, and C. C. Nelson. 2007. A case for “StopGo”: reprogramming translation to augment codon meaning of GGN by promoting unconventional termination (Stop) after addition of glycine and then allowing continued translation (Go). RNA 13803-810. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/E/01070911/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- G117/395/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 GM047498/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- C20035/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- GM47498/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- BB/E009093/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/E009093/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/E010709/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- C20418/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
