GTPase-mediated regulation of the unfolded protein response in Caenorhabditis elegans is dependent on the AAA+ ATPase CDC-48
- PMID: 18458060
- PMCID: PMC2447140
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.02252-07
GTPase-mediated regulation of the unfolded protein response in Caenorhabditis elegans is dependent on the AAA+ ATPase CDC-48
Abstract
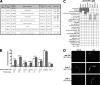
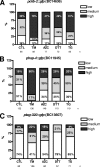
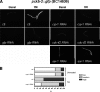
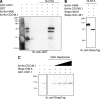
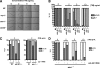
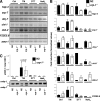
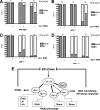
When endoplasmic reticulum (ER) homeostasis is perturbed, an adaptive mechanism is triggered and named the unfolded protein response (UPR). Thus far, three known UPR signaling branches (IRE-1, PERK, and ATF-6) mediate the reestablishment of ER functions but can also lead to apoptosis if ER stress is not alleviated. However, the understanding of the molecular mechanisms integrating the UPR to other ER functions, such as membrane traffic or endomembrane signaling, remains incomplete. We consequently sought to identify new regulators of UPR-dependent transcriptional mechanisms and focused on a family of proteins known to mediate, among other, ER-related functions: the small GTP-binding proteins of the RAS superfamily. To this end, we used transgenic UPR reporter Caenorhabditis elegans strains as a model to specifically silence small-GTPase expression. We show that the Rho subfamily member CRP-1 is an essential component of UPR-induced transcriptional events through its physical and genetic interactions with the AAA+ ATPase CDC-48. In addition, we describe a novel signaling module involving CRP-1 and CDC-48 which may directly link the UPR to DNA remodeling and transcription control.
Figures

References
-
- Ababou, M., S. Dutertre, Y. Lecluse, R. Onclercq, B. Chatton, and M. Amor-Gueret. 2000. ATM-dependent phosphorylation and accumulation of endogenous BLM protein in response to ionizing radiation. Oncogene 195955-5963. - PubMed
-
- Altan-Bonnet, N., R. Sougrat, and J. Lippincott-Schwartz. 2004. Molecular basis for Golgi maintenance and biogenesis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 16364-372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
