Sequence of conjugative plasmid pIP1206 mediating resistance to aminoglycosides by 16S rRNA methylation and to hydrophilic fluoroquinolones by efflux
- PMID: 18458128
- PMCID: PMC2443923
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01540-07
Sequence of conjugative plasmid pIP1206 mediating resistance to aminoglycosides by 16S rRNA methylation and to hydrophilic fluoroquinolones by efflux
Abstract
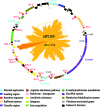
Self-transferable IncFI plasmid pIP1206, isolated from an Escherichia coli clinical isolate, carries two new resistance determinants: qepA, which confers resistance to hydrophylic fluoroquinolones by efflux, and rmtB, which specifies a 16S rRNA methylase conferring high-level aminoglycoside resistance. Analysis of the 168,113-bp sequence (51% G+C) revealed that pIP1206 was composed of several subregions separated by copies of insertion sequences. Of 151 open reading frames, 56 (37%) were also present in pRSB107, isolated from a bacterium in a sewage treatment plant. pIP1206 contained four replication regions (RepFIA, RepFIB, and two partial RepFII regions) and a transfer region 91% identical with that of pAPEC-O1-ColBM, a plasmid isolated from an avian pathogenic E. coli. A putative oriT region was found upstream from the transfer region. The antibiotic resistance genes tet(A), catA1, bla(TEM-1), rmtB, and qepA were clustered in a 33.5-kb fragment delineated by two IS26 elements that also carried a class 1 integron, including the sulI, qacEDelta1, aad4, and dfrA17 genes and Tn10, Tn21, and Tn3-like transposons. The plasmid also possessed a raffinose operon, an arginine deiminase pathway, a putative iron acquisition gene cluster, an S-methylmethionine metabolism operon, two virulence-associated genes, and a type I DNA restriction-modification (R-M) system. Three toxin/antitoxin systems and the R-M system ensured stabilization of the plasmid in the host bacteria. These data suggest that the mosaic structure of pIP1206 could have resulted from recombination between pRSB107 and a pAPEC-O1-ColBM-like plasmid, combined with structural rearrangements associated with acquisition of additional DNA by recombination and of mobile genetic elements by transposition.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The 120 592 bp IncF plasmid pRSB107 isolated from a sewage-treatment plant encodes nine different antibiotic-resistance determinants, two iron-acquisition systems and other putative virulence-associated functions.Microbiology (Reading). 2005 Apr;151(Pt 4):1095-1111. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27773-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2005. PMID: 15817778
-
Transferable resistance to aminoglycosides by methylation of G1405 in 16S rRNA and to hydrophilic fluoroquinolones by QepA-mediated efflux in Escherichia coli.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Jul;51(7):2464-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00143-07. Epub 2007 Apr 30. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17470656 Free PMC article.
-
The IncF plasmid pRSB225 isolated from a municipal wastewater treatment plant's on-site preflooder combining antibiotic resistance and putative virulence functions is highly related to virulence plasmids identified in pathogenic E. coli isolates.Plasmid. 2013 Mar;69(2):127-37. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2012.11.001. Epub 2012 Dec 2. Plasmid. 2013. PMID: 23212116
-
[Fluoroquinolones and Gram-negative bacteria: antimicrobial activity and mechanisms of resistance].Infez Med. 2008 Apr;16 Suppl2:5-11. Infez Med. 2008. PMID: 18843219 Review. Italian.
-
Transposon Tn21, flagship of the floating genome.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1999 Sep;63(3):507-22. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.63.3.507-522.1999. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10477306 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Complete sequence of pJIE186-2, a plasmid carrying multiple virulence factors from a sequence type 131 Escherichia coli O25 strain.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Jan;57(1):597-600. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01081-12. Epub 2012 Oct 15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23070168 Free PMC article.
-
The Arginine Deiminase Operon Is Responsible for a Fitness Trade-Off in Extended-Spectrum-β-Lactamase-Producing Strains of Escherichia coli.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Jul 25;63(8):e00635-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00635-19. Print 2019 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31138573 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular variation and horizontal gene transfer of the homocysteine methyltransferase gene mmuM and its distribution in clinical pathogens.Int J Biol Sci. 2015 Jan 1;11(1):11-21. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.10320. eCollection 2015. Int J Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25552925 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and characteristics of rmtB and qepA in Escherichia coli isolated from diseased animals in China.Front Microbiol. 2013 Jul 15;4:198. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00198. eCollection 2013. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23874331 Free PMC article.
-
Complete nucleotide sequence of plasmid pTN48, encoding the CTX-M-14 extended-spectrum β-lactamase from an Escherichia coli O102-ST405 strain.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Mar;55(3):1270-3. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01108-10. Epub 2010 Dec 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21173179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen, C., D. Krones, C. Ulmke, K. Schmid, and R. Benz. 1998. The porin RafY encoded by the raffinose plasmid pRSD2 of Escherichia coli forms a general diffusion pore and not a carbohydrate-specific porin. Eur. J. Biochem. 254:679-684. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

