Cdc14B depletion leads to centriole amplification, and its overexpression prevents unscheduled centriole duplication
- PMID: 18458157
- PMCID: PMC2364701
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200710127
Cdc14B depletion leads to centriole amplification, and its overexpression prevents unscheduled centriole duplication
Abstract
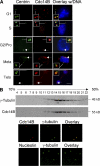
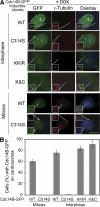
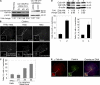
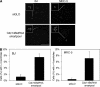
Centrosome duplication is tightly controlled in coordination with DNA replication. The molecular mechanism of centrosome duplication remains unclear. Previous studies found that a fraction of human proline-directed phosphatase Cdc14B associates with centrosomes. However, Cdc14B's involvement in centrosome cycle control has never been explored. Here, we show that depletion of Cdc14B by RNA interference leads to centriole amplification in both HeLa and normal human fibroblast BJ and MRC-5 cells. Induction of Cdc14B expression through a regulatable promoter significantly attenuates centriole amplification in prolonged S phase-arrested cells and proteasome inhibitor Z-L(3)VS-treated cells. This inhibitory function requires centriole-associated Cdc14B catalytic activity. Together, these results suggest a potential function for Cdc14B phosphatase in maintaining the fidelity of centrosome duplication cycle.
Figures

References
-
- Ashida, S., H. Nakagawa, T. Katagiri, M. Furihata, M. Iiizumi, Y. Anazawa, T. Tsunoda, R. Takata, K. Kasahara, T. Miki, et al. 2004. Molecular features of the transition from prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) to prostate cancer: genome-wide gene-expression profiles of prostate cancers and PINs. Cancer Res. 64:5963–5972. - PubMed
-
- Bembenek, J., J. Kang, C. Kurischko, B. Li, J.R. Raab, K.D. Belanger, F.C. Luca, and H. Yu. 2005. Crm1-mediated nuclear export of Cdc14 is required for the completion of cytokinesis in budding yeast. Cell Cycle. 4:961–971. - PubMed
-
- Boutros, R., V. Lobjois, and B. Ducommun. 2007. CDC25B involvement in the centrosome duplication cycle and in microtubule nucleation. Cancer Res. 67:11557–11564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

