Human ApoD, an apolipoprotein up-regulated in neurodegenerative diseases, extends lifespan and increases stress resistance in Drosophila
- PMID: 18458334
- PMCID: PMC2374552
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0800896105
Human ApoD, an apolipoprotein up-regulated in neurodegenerative diseases, extends lifespan and increases stress resistance in Drosophila
Abstract
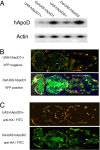
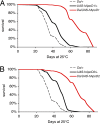
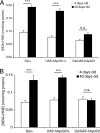
Apolipoprotein D (ApoD) expression increases in several neurological disorders and in spinal cord injury. We provide a report of a physiological role for human ApoD (hApoD): Flies overexpressing hApoD are long-lived and protected against stress conditions associated with aging and neurodegeneration, including hyperoxia, dietary paraquat, and heat stress. We show that the fly ortholog, Glial Lazarillo, is strongly up-regulated in response to these extrinsic stresses and also can protect in vitro-cultured cells in situations modeling Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD). In adult flies, hApoD overexpression reduces age-associated lipid peroxide accumulation, suggesting a proximal mechanism of action. Similar data obtained in the mouse [Ganfornina, M.D., et al., (2008) Apolipoprotein D is involved in the mechanisms regulating protection from oxidative stress. Aging Cell 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2008.00395.] as well as in plants (Charron et al., personal communication) suggest that ApoD and its orthologs play an evolutionarily conserved role in response to stress, possibly managing or preventing lipid peroxidation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Sex-dependent modulation of longevity by two Drosophila homologues of human Apolipoprotein D, GLaz and NLaz.Exp Gerontol. 2011 Jul;46(7):579-89. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2011.02.014. Epub 2011 Mar 3. Exp Gerontol. 2011. PMID: 21376794
-
Loss of glial lazarillo, a homolog of apolipoprotein D, reduces lifespan and stress resistance in Drosophila.Curr Biol. 2006 Apr 4;16(7):680-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.03.024. Curr Biol. 2006. PMID: 16581513
-
Apolipoprotein D is involved in the mechanisms regulating protection from oxidative stress.Aging Cell. 2008 Aug;7(4):506-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2008.00395.x. Epub 2008 Apr 14. Aging Cell. 2008. PMID: 18419796 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein D takes center stage in the stress response of the aging and degenerative brain.Neurobiol Aging. 2014 Jul;35(7):1632-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.01.148. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Neurobiol Aging. 2014. PMID: 24612673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein D.Gene. 2020 Sep 25;756:144874. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144874. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32554047 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Site-specific interaction between α-synuclein and membranes probed by NMR-observed methionine oxidation rates.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Feb 27;135(8):2943-6. doi: 10.1021/ja312415q. Epub 2013 Feb 14. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 23398174 Free PMC article.
-
Fecal proteomics of wild capuchins reveals impacts of season, diet, age, and, sex on gut physiology.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 21:2025.06.16.659980. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.16.659980. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40666882 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Molecular dynamics analysis of apolipoprotein-D-lipid hydroperoxide interactions: mechanism for selective oxidation of Met-93.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e34057. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034057. Epub 2012 Mar 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22479522 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein D Overexpression Protects Against Kainate-Induced Neurotoxicity in Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Aug;54(6):3948-3963. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9920-4. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27271124 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-specific lipoprotein receptors interact with astrocyte derived apolipoprotein and mediate neuron-glia lipid shuttling.Nat Commun. 2021 Apr 23;12(1):2408. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22751-7. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33893307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rassart E, et al. Apolipoprotein D. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1482:185–198. - PubMed
-
- Provost PR, et al. Localization of the major sites of rabbit apolipoprotein D gene transcription by in situ hybridization. J Lipid Res. 1991;32:1959–1970. - PubMed
-
- Provost PR, Weech PK, Tremblay NM, Marcel YL, Rassart E. Molecular characterization and differential mRNA tissue distribution of rabbit apolipoprotein D. J Lipid Res. 1990;31:2057–2065. - PubMed
-
- Weech PK, et al. Apolipoprotein D: An atypical apolipoprotein. Prog Lipid Res. 1991;30:259–266. - PubMed
-
- Terrisse L, et al. Increased levels of apolipoprotein D in cerebrospinal fluid and hippocampus of Alzheimer's patients. J Neurochem. 1998;71:1643–1650. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

