Residue-level interrogation of macromolecular crowding effects on protein stability
- PMID: 18459780
- PMCID: PMC2435214
- DOI: 10.1021/ja8005995
Residue-level interrogation of macromolecular crowding effects on protein stability
Abstract
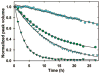
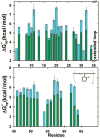
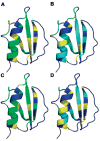
Theory predicts that macromolecular crowding affects protein behavior, but experimental confirmation is scant. Herein, we report the first residue-level interrogation of the effects of macromolecular crowding on protein stability. We observe up to a 100-fold increase in the stability, as measured by the equilibrium constant for folding, for the globular protein chymotrypsin inhibitor 2 (CI2) in concentrations of the cosolute poly(vinylpyrrolidone) (PVP) that mimic the protein concentration in cells. We show that the increased stability is caused by the polymeric nature of PVP and that the degree of stabilization depends on both the location of the individual residue in the protein structure and the PVP concentration. Our data reinforce the assertion that macromolecular crowding stabilizes the protein by destabilizing its unfolded states.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

