Phosphorylation of the JAK2-STAT5 pathway in response to acute aerobic exercise
- PMID: 18461004
- PMCID: PMC5008036
- DOI: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181690760
Phosphorylation of the JAK2-STAT5 pathway in response to acute aerobic exercise
Abstract
Growth hormone (GH) is a powerful stimulator of the Janus kinase 2 (JAK2)-signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) pathway. Acute exercise is a known stimulus for GH secretion.
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to determine the phosphorylation of the JAK2-STAT5 pathway in human skeletal muscle in response to acute aerobic exercise.
Methods: Eleven young (22.5 +/- 0.6, mean +/- SE), healthy, aerobically trained males performed 30 min of cycling at 70% V O2max. Blood samples were collected at 10- to 15-min intervals and analyzed for human GH, immunofunctional (IF) GH, GH binding protein, and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I). Muscle biopsies were taken from the vastus lateralis before exercise, immediately after exercise, as well as, 30 and 60 min postexercise. Muscle samples were analyzed for changes in JAK2 and STAT5 tyrosine phosphorylation, as well as changes in JAK2 and STAT5 protein content.
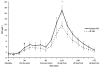
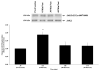
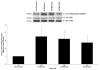
Results: Multivariate ANOVA with post hoc comparisons demonstrated that GH and IF GH were significantly elevated immediately after exercise compared with preexercise (P < 0.001). Exercise significantly increased the phosphorylation of JAK2 immediately after exercise (P = 0.004). A trend toward increasing levels of STAT5 phosphorylation was observed immediately after exercise (P = 0.08) and was significantly elevated 30 min after exercise (P = 0.002), compared with preexercise levels. Muscle JAK2 and STAT5 protein content did not change.
Conclusion: The results demonstrate that the JAK2-STAT5 pathway is activated in response to acute aerobic exercise in human skeletal muscle and suggests that the exercise-induced release of GH may play a role in the activation of this pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High concentrations of fatty acids and β-hydroxybutyrate impair the growth hormone-mediated hepatic JAK2-STAT5 pathway in clinically ketotic cows.J Dairy Sci. 2018 Apr;101(4):3476-3487. doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-13234. Epub 2018 Feb 2. J Dairy Sci. 2018. PMID: 29398030
-
Inherent growth hormone resistance in the skeletal muscle of the fine flounder is modulated by nutritional status and is characterized by high contents of truncated GHR, impairment in the JAK2/STAT5 signaling pathway, and low IGF-I expression.Endocrinology. 2012 Jan;153(1):283-94. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-1313. Epub 2011 Oct 25. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22028448
-
Functional collaboration of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R), but not insulin receptor (IR), with acute GH signaling in mouse calvarial cells.Endocrinology. 2014 Mar;155(3):1000-9. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1732. Epub 2013 Jan 1. Endocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24302626 Free PMC article.
-
Human growth disorders associated with impaired GH action: Defects in STAT5B and JAK2.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021 Jan 1;519:111063. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2020.111063. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 33122102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic growth hormone - JAK2 - STAT5 signalling: Metabolic function, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma progression.Cytokine. 2019 Dec;124:154569. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.10.010. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Cytokine. 2019. PMID: 30389231 Review.
Cited by
-
Lactate-induced lactylation in skeletal muscle is associated with insulin resistance in humans.Front Physiol. 2022 Aug 30;13:951390. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.951390. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36111162 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Polymorphism in the Janus Kinase 2 (JAK2) Gene and Selected Performance Traits in Cattle and Sheep.Animals (Basel). 2023 Jul 31;13(15):2470. doi: 10.3390/ani13152470. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37570280 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal muscle growth and fiber composition in mice are regulated through the transcription factors STAT5a/b: linking growth hormone to the androgen receptor.FASEB J. 2009 Sep;23(9):3140-8. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-128215. Epub 2009 May 5. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 19417088 Free PMC article.
-
Trypanosoma cruzi Promotes Transcriptomic Remodeling of the JAK/STAT Signaling and Cell Cycle Pathways in Myoblasts.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Jun 17;10:255. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00255. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32626662 Free PMC article.
-
Response of the JAK-STAT pathway to mammalian hibernation in 13-lined ground squirrel striated muscle.Mol Cell Biochem. 2016 Mar;414(1-2):115-27. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2665-6. Epub 2016 Feb 17. Mol Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26885984
References
-
- Asada N, Takahashi Y, Wada M, et al. GH induced lipolysis stimulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes stably expressing hGHR: analysis on signaling pathway and activity of 20K hGH. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000;162:121–9. - PubMed
-
- Bodary PF, Pate RR, Wu QF, McMillan GS. Effects of acute exercise on plasma erythropoietin levels in trained runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1999;31(4):543–6. - PubMed
-
- Deldicque L, Louis M, Theisen D, et al. Increased IGF mRNA in human skeletal muscle after creatine supplementation. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005;37(5):731–6. - PubMed
-
- Fan H, Turck CW, Derynck R. Characterization of growth factor-induced serine phosphorylation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha converting enzyme and of an alternatively translated polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:18617–27. - PubMed
-
- Fisker S, Kristensen K, Rosenfalck AM, et al. Gene expression a truncated and the full-length growth hormone (GH) receptor in subcutaneous fat and skeletal muscle in GH-deficient adults: impact of GH treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:792–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

