Systematic identification of mRNAs recruited to argonaute 2 by specific microRNAs and corresponding changes in transcript abundance
- PMID: 18461144
- PMCID: PMC2330160
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002126
Systematic identification of mRNAs recruited to argonaute 2 by specific microRNAs and corresponding changes in transcript abundance
Erratum in
- PLoS ONE. 2008;3(11).doi.org/10.1371/annotation/c8902b4c-30fc-42e7-b506-fc756a3cdd4e
Abstract
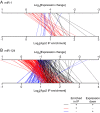
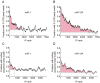
microRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that regulate mRNA stability and translation through the action of the RNAi-induced silencing complex (RISC). Our current understanding of miRNA function is inferred largely from studies of the effects of miRNAs on steady-state mRNA levels and from seed match conservation and context in putative targets. Here we have taken a more direct approach to these issues by comprehensively assessing the miRNAs and mRNAs that are physically associated with Argonaute 2 (Ago2), which is a core RISC component. We transfected HEK293T cells with epitope-tagged Ago2, immunopurified Ago2 together with any associated miRNAs and mRNAs, and quantitatively determined the levels of these RNAs by microarray analyses. We found that Ago2 immunopurified samples contained a representative repertoire of the cell's miRNAs and a select subset of the cell's total mRNAs. Transfection of the miRNAs miR-1 and miR-124 caused significant changes in the association of scores of mRNAs with Ago2. The mRNAs whose association with Ago2 increased upon miRNA expression were much more likely to contain specific miRNA seed matches and to have their overall mRNA levels decrease in response to the miRNA transfection than expected by chance. Hundreds of mRNAs were recruited to Ago2 by each miRNA via seed sequences in 3'-untranslated regions and coding sequences and a few mRNAs appear to be targeted via seed sequences in 5'-untranslated regions. Microarray analysis of Ago2 immunopurified samples provides a simple, direct method for experimentally identifying the targets of miRNAs and for elucidating roles of miRNAs in cellular regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
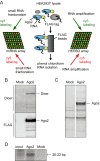
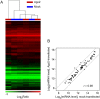
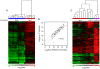
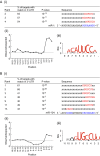

References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Carthew RW. Gene regulation by microRNAs. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006;16:203–208. - PubMed
-
- Chen PY, Meister G. microRNA-guided posttranscriptional gene regulation. Biol Chem. 2005;386:1205–1218. - PubMed
-
- Farh KK, Grimson A, Jan C, Lewis BP, Johnston WK, et al. The widespread impact of mammalian MicroRNAs on mRNA repression and evolution. Science. 2005;310:1817–1821. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

