The herbicide atrazine activates endocrine gene networks via non-steroidal NR5A nuclear receptors in fish and mammalian cells
- PMID: 18461179
- PMCID: PMC2362696
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002117
The herbicide atrazine activates endocrine gene networks via non-steroidal NR5A nuclear receptors in fish and mammalian cells
Abstract
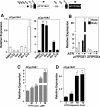
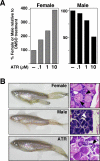
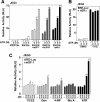
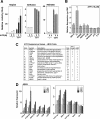
Atrazine (ATR) remains a widely used broadleaf herbicide in the United States despite the fact that this s-chlorotriazine has been linked to reproductive abnormalities in fish and amphibians. Here, using zebrafish we report that environmentally relevant ATR concentrations elevated zcyp19a1 expression encoding aromatase (2.2 microg/L), and increased the ratio of female to male fish (22 microg/L). ATR selectively increased zcyp19a1, a known gene target of the nuclear receptor SF-1 (NR5A1), whereas zcyp19a2, which is estrogen responsive, remained unchanged. Remarkably, in mammalian cells ATR functions in a cell-specific manner to upregulate SF-1 targets and other genes critical for steroid synthesis and reproduction, including Cyp19A1, StAR, Cyp11A1, hCG, FSTL3, LHss, INHalpha, alphaGSU, and 11ss-HSD2. Our data appear to eliminate the possibility that ATR directly affects SF-1 DNA- or ligand-binding. Instead, we suggest that the stimulatory effects of ATR on the NR5A receptor subfamily (SF-1, LRH-1, and zff1d) are likely mediated by receptor phosphorylation, amplification of cAMP and PI3K signaling, and possibly an increase in the cAMP-responsive cellular kinase SGK-1, which is known to be upregulated in infertile women. Taken together, we propose that this pervasive and persistent environmental chemical alters hormone networks via convergence of NR5A activity and cAMP signaling, to potentially disrupt normal endocrine development and function in lower and higher vertebrates.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Herbicide atrazine activates SF-1 by direct affinity and concomitant co-activators recruitments to induce aromatase expression via promoter II.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Apr 20;355(4):1012-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.02.062. Epub 2007 Feb 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17331471
-
Atrazine enhances progesterone production through activation of multiple signaling pathways in FSH-stimulated rat granulosa cells: evidence for premature luteinization.Biol Reprod. 2014 Nov;91(5):124. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.114.122606. Epub 2014 Sep 24. Biol Reprod. 2014. PMID: 25253736
-
Atrazine-induced environmental nephrosis was mitigated by lycopene via modulating nuclear xenobiotic receptors-mediated response.J Nutr Biochem. 2018 Jan;51:80-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.09.006. Epub 2017 Sep 21. J Nutr Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29107825
-
The Orphan Nuclear Receptors Steroidogenic Factor-1 and Liver Receptor Homolog-1: Structure, Regulation, and Essential Roles in Mammalian Reproduction.Physiol Rev. 2019 Apr 1;99(2):1249-1279. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00019.2018. Physiol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30810078 Review.
-
Effects of atrazine on fish, amphibians, and aquatic reptiles: a critical review.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2008;38(9):721-72. doi: 10.1080/10408440802116496. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18941967 Review.
Cited by
-
A clash of old and new scientific concepts in toxicity, with important implications for public health.Environ Health Perspect. 2009 Nov;117(11):1652-5. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0900887. Epub 2009 Jul 30. Environ Health Perspect. 2009. PMID: 20049113 Free PMC article.
-
Pesticide Pollution: Detrimental Outcomes and Possible Mechanisms of Fish Exposure to Common Organophosphates and Triazines.J Xenobiot. 2022 Sep 2;12(3):236-265. doi: 10.3390/jox12030018. J Xenobiot. 2022. PMID: 36135714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vivo Screening Using Transgenic Zebrafish Embryos Reveals New Effects of HDAC Inhibitors Trichostatin A and Valproic Acid on Organogenesis.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 22;11(2):e0149497. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149497. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26900852 Free PMC article.
-
Human male infertility associated with mutations in NR5A1 encoding steroidogenic factor 1.Am J Hum Genet. 2010 Oct 8;87(4):505-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.09.009. Am J Hum Genet. 2010. PMID: 20887963 Free PMC article.
-
Atrazine exposure affects longevity, development time and body size in Drosophila melanogaster.J Insect Physiol. 2016 Aug-Sep;91-92:18-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2016.06.006. Epub 2016 Jun 15. J Insect Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27317622 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crews D, McLachlan JA. Epigenetics, evolution, endocrine disruption, health, and disease. Endocrinology. 2006;147:S4–10. - PubMed
-
- Gaido KW, Maness SC, McDonnell DP, Dehal SS, Kupfer D, et al. Interaction of methoxychlor and related compounds with estrogen receptor alpha and beta, and androgen receptor: structure-activity studies. Mol Pharmacol. 2000;58:852–858. - PubMed
-
- Singleton DW, Feng Y, Chen Y, Busch SJ, Lee AV, et al. Bisphenol-A and estradiol exert novel gene regulation in human MCF-7 derived breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2004;221:47–55. - PubMed
-
- Singleton DW, Feng Y, Yang J, Puga A, Lee AV, et al. Gene expression profiling reveals novel regulation by bisphenol-A in estrogen receptor-alpha-positive human cells. Environ Res. 2006;100:86–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

