Synaptic input to dentate granule cell basal dendrites in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy
- PMID: 18461605
- PMCID: PMC2667124
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.21745
Synaptic input to dentate granule cell basal dendrites in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy
Abstract
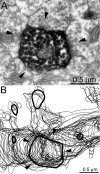
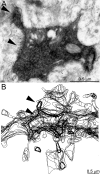
In patients with temporal lobe epilepsy some dentate granule cells develop basal dendrites. The extent of excitatory synaptic input to basal dendrites is unclear, nor is it known whether basal dendrites receive inhibitory synapses. We used biocytin to intracellularly label individual granule cells with basal dendrites in epileptic pilocarpine-treated rats. An average basal dendrite had 3.9 branches, was 612 microm long, and accounted for 16% of a cell's total dendritic length. In vivo intracellular labeling and postembedding GABA-immunocytochemistry were used to evaluate synapses with basal dendrites reconstructed from serial electron micrographs. An average of 7% of 1,802 putative synapses were formed by GABA-positive axon terminals, indicating synaptogenesis by interneurons. Ninety-three percent of the identified synapses were GABA-negative. Most GABA-negative synapses were with spines, but at least 10% were with dendritic shafts. Multiplying basal dendrite length/cell and synapse density yielded an estimate of 180 inhibitory and 2,140 excitatory synapses per granule cell basal dendrite. Based on previous estimates of synaptic input to granule cells in control rats, these findings suggest an average basal dendrite receives approximately 14% of the total inhibitory and 19% of excitatory synapses of a cell. These findings reveal that basal dendrites are a novel source of inhibitory input, but they primarily receive excitatory synapses.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Initial loss but later excess of GABAergic synapses with dentate granule cells in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy.J Comp Neurol. 2010 Mar 1;518(5):647-67. doi: 10.1002/cne.22235. J Comp Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20034063 Free PMC article.
-
Status epilepticus-induced hilar basal dendrites on rodent granule cells contribute to recurrent excitatory circuitry.J Comp Neurol. 2000 Dec 11;428(2):240-53. doi: 10.1002/1096-9861(20001211)428:2<240::aid-cne4>3.0.co;2-q. J Comp Neurol. 2000. PMID: 11064364
-
Reduced inhibition of dentate granule cells in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy.J Neurosci. 2003 Mar 15;23(6):2440-52. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-06-02440.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12657704 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic connections of hilar basal dendrites of dentate granule cells in a neonatal hypoxia model of epilepsy.Epilepsia. 2012 Jun;53 Suppl 1:98-108. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2012.03481.x. Epilepsia. 2012. PMID: 22612814 Review.
-
Synapses formed by normal and abnormal hippocampal mossy fibers.Cell Tissue Res. 2006 Nov;326(2):361-7. doi: 10.1007/s00441-006-0269-2. Epub 2006 Jul 4. Cell Tissue Res. 2006. PMID: 16819624 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased cell-intrinsic excitability induces synaptic changes in new neurons in the adult dentate gyrus that require Npas4.J Neurosci. 2013 May 1;33(18):7928-40. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1571-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23637184 Free PMC article.
-
Morphologic integration of hilar ectopic granule cells into dentate gyrus circuitry in the pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy.J Comp Neurol. 2011 Aug 1;519(11):2175-92. doi: 10.1002/cne.22623. J Comp Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21455997 Free PMC article.
-
Repositioning of Somatic Golgi Apparatus Is Essential for the Dendritic Establishment of Adult-Born Hippocampal Neurons.J Neurosci. 2018 Jan 17;38(3):631-647. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1217-17.2017. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29217690 Free PMC article.
-
Rabies tracing of birthdated dentate granule cells in rat temporal lobe epilepsy.Ann Neurol. 2017 Jun;81(6):790-803. doi: 10.1002/ana.24946. Ann Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28470680 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous integration of adult-generated granule cells into the epileptic brain.J Neurosci. 2011 Jan 5;31(1):105-17. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2728-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21209195 Free PMC article.
References
-
- André V, Marescaux C, Nehlig A, Fritschy JM. Alterations of hippocampal GABAergic system contribute to development of spontaneous recurrent seizures in the rat lithium-pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Hippocampus. 2001;11:452–468. - PubMed
-
- Austin JE, Buckmaster PS. Recurrent excitation of granule cells with basal dendrites and low interneuron density and inhibitory postsynaptic current frequency in the dentate gyrus of macaque monkeys. J Comp Neurol. 2004;476:205–218. - PubMed

