Impact of round-the-clock, rapid oral fluid HIV testing of women in labor in rural India
- PMID: 18462011
- PMCID: PMC2365974
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050092
Impact of round-the-clock, rapid oral fluid HIV testing of women in labor in rural India
Abstract
Background: Testing pregnant women for HIV at the time of labor and delivery is the last opportunity for prevention of mother-to-child HIV transmission (PMTCT) measures, particularly in settings where women do not receive adequate antenatal care. However, HIV testing and counseling of pregnant women in labor is a challenge, especially in resource-constrained settings. In India, many rural women present for delivery without any prior antenatal care. Those who do get antenatal care are not always tested for HIV, because of deficiencies in the provision of HIV testing and counseling services. In this context, we investigated the impact of introducing round-the-clock, rapid, point-of-care HIV testing and counseling in a busy labor ward at a tertiary care hospital in rural India.
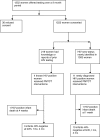
Methods and findings: After they provided written informed consent, women admitted to the labor ward of a rural teaching hospital in India were offered two rapid tests on oral fluid and finger-stick specimens (OraQuick Rapid HIV-1/HIV-2 tests, OraSure Technologies). Simultaneously, venous blood was drawn for conventional HIV ELISA testing. Western blot tests were performed for confirmatory testing if women were positive by both rapid tests and dual ELISA, or where test results were discordant. Round-the-clock (24 h, 7 d/wk) abbreviated prepartum and extended postpartum counseling sessions were offered as part of the testing strategy. HIV-positive women were administered PMTCT interventions. Of 1,252 eligible women (age range 18 y to 38 y) approached for consent over a 9 mo period in 2006, 1,222 (98%) accepted HIV testing in the labor ward. Of these, 1,003 (82%) women presented with either no reports or incomplete reports of prior HIV testing results at the time of admission to the labor ward. Of 1,222 women, 15 were diagnosed as HIV-positive (on the basis of two rapid tests, dual ELISA and Western blot), yielding a seroprevalence of 1.23% (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.61%-1.8%). Of the 15 HIV test-positive women, four (27%) had presented with reported HIV status, and 11 (73%) new cases of HIV infection were detected due to rapid testing in the labor room. Thus, 11 HIV-positive women received PMTCT interventions on account of round-the-clock rapid HIV testing and counseling in the labor room. While both OraQuick tests (oral and finger-stick) were 100% specific, one false-negative result was documented (with both oral fluid and finger-stick specimens). Of the 15 HIV-infected women who delivered, 13 infants were HIV seronegative at birth and at 1 and 4 mo after delivery; two HIV-positive infants died within a month of delivery.
Conclusions: In a busy rural labor ward setting in India, we demonstrated that it is feasible to introduce a program of round-the-clock rapid HIV testing, including prepartum and extended postpartum counseling sessions. Our data suggest that the availability of round-the-clock rapid HIV testing resulted in successful documentation of HIV serostatus in a large proportion (82%) of rural women who were unaware of their HIV status when admitted to the labor room. In addition, 11 (73%) of a total of 15 HIV-positive women received PMTCT interventions because of round-the-clock rapid testing in the labor ward. These findings are relevant for PMTCT programs in developing countries.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Is HIV screening in the labor and delivery unit feasible and acceptable in low-income settings?PLoS Med. 2008 May 6;5(5):e107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050107. PLoS Med. 2008. PMID: 18462015 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Is HIV screening in the labor and delivery unit feasible and acceptable in low-income settings?PLoS Med. 2008 May 6;5(5):e107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050107. PLoS Med. 2008. PMID: 18462015 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of diagnostic accuracy, feasibility and client preference for rapid oral fluid-based diagnosis of HIV infection in rural India.PLoS One. 2007 Apr 11;2(4):e367. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000367. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17426815 Free PMC article.
-
[HIV testing among women in delivery rooms in Lubumbashi, Democratic Republic of the Congo: a catch-up strategy for prevention of mother-to-child transmission].Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 2013 Feb;61(1):21-7. doi: 10.1016/j.respe.2012.05.008. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 2013. PMID: 23337841 French.
-
Rapid testing at labor and delivery to prevent mother-to-child HIV transmission in developing settings: issues and challenges.Womens Health (Lond). 2009 Jan;5(1):55-62. doi: 10.2217/17455057.5.1.55. Womens Health (Lond). 2009. PMID: 19102641 Review.
-
Approaches for scaling up human immunodeficiency virus testing and counseling in prevention of mother-to-child human immunodeficiency virus transmission settings in resource-limited countries.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007 Sep;197(3 Suppl):S83-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2007.03.006. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007. PMID: 17825654 Review.
Cited by
-
Point of care HIV testing with oral fluid among returnee migrants in a rural area of Bangladesh.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2016 Mar;11 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S52-8. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000267. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2016. PMID: 26945144 Free PMC article.
-
Field-based video pre-test counseling, oral testing, and telephonic post-test counseling: implementation of an HIV field testing package among high-risk Indian men.AIDS Educ Prev. 2012 Aug;24(4):309-26. doi: 10.1521/aeap.2012.24.4.309. AIDS Educ Prev. 2012. PMID: 22827901 Free PMC article.
-
A pilot study to assess the performance of a rapid ultrasound particle agglutination method for the detection of HIV antibodies.J Immunoassay Immunochem. 2022 Mar 4;43(2):176-191. doi: 10.1080/15321819.2021.1981376. Epub 2021 Oct 26. J Immunoassay Immunochem. 2022. PMID: 34697982 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating HIV screening into routine health care in resource-limited settings.Clin Infect Dis. 2010 May 15;50 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S77-84. doi: 10.1086/651477. Clin Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20397960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Field evaluation of diagnostic accuracy of an oral fluid rapid test for HIV, tested at point-of-service sites in rural Zimbabwe.AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2009 Jul;23(7):571-6. doi: 10.1089/apc.2008.0225. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2009. PMID: 19530953 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UNAIDS. Document Number UNAIDS/06.20E. Geneva: 2006. 2006 report on the global AIDS epidemic: executive summary / UNAIDS. Available at: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/unaids/2006/9291735116_eng.pdf. Accessed 31 March 2008.
-
- Brocklehurst P, Volmink J. Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev: CD003510. 2002. - PubMed
-
- Kourtis AP, Lee FK, Abrams EJ, Jamieson DJ, Bulterys M. Mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1: timing and implications for prevention. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006;6:726–732. - PubMed
-
- Pant Pai N. Oral fluid-based rapid HIV testing: issues, challenges and research directions. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2007;7(4):325–328. - PubMed