3D micro-CT imaging of the postmortem brain
- PMID: 18462802
- PMCID: PMC2693019
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2008.03.006
3D micro-CT imaging of the postmortem brain
Abstract
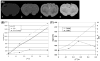
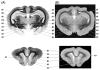
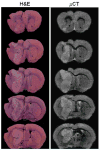
Magnetic resonance microscopy (microMRI) is becoming an important tool for non-destructive analysis of fixed brain tissue. However, unlike MRI, X-ray computed tomography (CT) scans show little native soft tissue contrast. In this paper, we explored the use of contrast enhanced (brains immersion stained in iodinated CT contrast media) micro-CT (microCT) for high resolution 3D imaging of fixed normal and pathological brains, compared to microMRI and standard histopathology. An optimum iodine concentration of 0.27 M resulted in excellent contrast between gray and white matter in normal brain and a wide range of anatomical structures were identified. In glioma bearing mouse brains, there was clear deliniation of tumor margin which closely matched that seen on histopathology sections. microCT tumor volume was strongly correlated with histopathology volume. Our data suggests that microCT image contrast in the immersion-stained brains is related to axonal density and myelin content. Compared to traditional histopathology, our microCT approach is relatively rapid and less labor intensive. In addition, compared to microMRI, microCT is robust and requires much lower equipment and maintenance costs. For simple measurements, such as tumor volume and non-destructive postmortem brain screening, microCT may prove to be a valuable alternative to standard histopathology or microMRI.
Figures


References
-
- Barck KH, Lee WP, Diehl LJ, Ross J, Gribling P, Zhang Y, Nguyen K, van Bruggen N, Hurst S, Carano RA. Quantification of cortical bone loss and repair for therapeutic evaluation in collagen-induced arthritis, by micro-computed tomography and automated image analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:3377–86. - PubMed
-
- Boyko OB, Alston SR, Fuller GN, Hulette CM, Johnson GA, Burger PC. Utility of postmortem magnetic resonance imaging in clinical neuropathology. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1994;118:219–25. - PubMed
-
- D’Arceuil H, Liu C, Levitt P, Thompson B, Kosofsky B, de Crespigny A. Three-Dimensional High-Resolution Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Tractography of the Developing Rabbit Brain. Dev Neurosci. 2007a - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

