Molecular determinants of species-specific activation or blockade of TRPA1 channels
- PMID: 18463259
- PMCID: PMC6670736
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0047-08.2008
Molecular determinants of species-specific activation or blockade of TRPA1 channels
Abstract
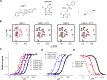
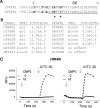
TRPA1 is an excitatory, nonselective cation channel implicated in somatosensory function, pain, and neurogenic inflammation. Through covalent modification of cysteine and lysine residues, TRPA1 can be activated by electrophilic compounds, including active ingredients of pungent natural products (e.g., allyl isothiocyanate), environmental irritants (e.g., acrolein), and endogenous ligands (4-hydroxynonenal). However, how covalent modification leads to channel opening is not understood. Here, we report that electrophilic, thioaminal-containing compounds [e.g., CMP1 (4-methyl-N-[2,2,2-trichloro-1-(4-nitro-phenylsulfanyl)-ethyl]-benzamide)] covalently modify cysteine residues but produce striking species-specific effects [i.e., activation of rat TRPA1 (rTRPA1) and blockade of human TRPA1 (hTRPA1) activation by reactive and nonreactive agonists]. Through characterizing rTRPA1 and hTRPA1 chimeric channels and point mutations, we identified several residues in the upper portion of the S6 transmembrane domains as critical determinants of the opposite channel gating: Ala-946 and Met-949 of rTRPA1 determine channel activation, whereas equivalent residues of hTRPA1 (Ser-943 and Ile-946) determine channel block. Furthermore, side-chain replacements at these critical residues profoundly affect channel function. Therefore, our findings reveal a molecular basis of species-specific channel gating and provide novel insights into how TRPA1 respond to stimuli.
Figures



References
-
- Bandell M, Story GM, Hwang SW, Viswanath V, Eid SR, Petrus MJ, Earley TJ, Patapoutian A. Noxious cold ion channel TRPA1 is activated by pungent compounds and bradykinin. Neuron. 2004;41:849–857. - PubMed
-
- Bandell M, Dubin AE, Petrus MJ, Orth A, Mathur J, Hwang SW, Patapoutian A. High-throughput random mutagenesis screen reveals TRPM8 residues specifically required for activation by menthol. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:493–500. - PubMed
-
- Bautista DM, Jordt SE, Nikai T, Tsuruda PR, Read AJ, Poblete J, Yamoah EN, Basbaum AI, Julius D. TRPA1 mediates the inflammatory actions of environmental irritants and proalgesic agents. Cell. 2006;124:1269–1282. - PubMed
-
- Berneche S, Roux B. A gate in the selectivity filter of potassium channels. Structure. 2005;13:591–600. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
