Alendronate reduces bone toughness of ribs without significantly increasing microdamage accumulation in dogs following 3 years of daily treatment
- PMID: 18463913
- PMCID: PMC2698704
- DOI: 10.1007/s00223-008-9131-8
Alendronate reduces bone toughness of ribs without significantly increasing microdamage accumulation in dogs following 3 years of daily treatment
Abstract
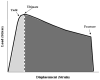
Reduced bone toughness, the energy absorption capacity of the tissue, has been consistently documented in vertebrae of animals treated with a wide range of bisphosphonate doses. Data regarding toughness changes in the rib are conflicting, with one report showing no effect and another showing a significant reduction following treatment of beagle dogs with high doses of bisphosphonates. The goal of this study was to evaluate changes in bone toughness and various other tissue-level properties of the rib following 3 years of bisphosphonate treatment with doses at and above those used to treat osteoporosis. Skeletally mature intact beagle dogs were treated daily for 3 years with vehicle (VEH), alendronate 0.2 mg/kg (ALN0.2), or alendronate 1.0 mg/kg (ALN1.0). The lower ALN dose approximates, on a milligram per kilogram basis, that used for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis, with the higher dose being five times higher. Ribs were assessed for biomechanical properties, bone turnover rate, microdamage, density, and geometry. Toughness was significantly lower with ALN1.0 (-33%) but not ALN0.2 (-19%) compared to VEH, while neither ultimate stress nor modulus differed among the groups. Bone density, geometry, and structural biomechanical properties were similar among the three groups. There was no significant difference in overall microdamage accumulation among the groups. Intracortical bone formation rate was significantly lower than VEH in both ALN groups (-69% to -90%). These data show that while rib cortical bone experiences significant reductions in turnover following bisphosphonate treatment, it is only in animals treated with doses above those used to treat osteoporosis that toughness is significantly compromised.
Figures
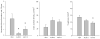
Similar articles
-
Three years of alendronate treatment results in similar levels of vertebral microdamage as after one year of treatment.J Bone Miner Res. 2007 Nov;22(11):1759-65. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.070720. J Bone Miner Res. 2007. PMID: 17663638
-
Suppressed bone turnover by bisphosphonates increases microdamage accumulation and reduces some biomechanical properties in dog rib.J Bone Miner Res. 2000 Apr;15(4):613-20. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2000.15.4.613. J Bone Miner Res. 2000. PMID: 10780852
-
Mandible matrix necrosis in beagle dogs after 3 years of daily oral bisphosphonate treatment.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008 May;66(5):987-94. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2008.01.038. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008. PMID: 18423290 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of antiresorptive therapy on the structural and material properties of bone strength].Clin Calcium. 2016 Jan;26(1):107-15. Clin Calcium. 2016. PMID: 26728537 Review. Japanese.
-
Bisphosphonates for prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis.Dan Med Bull. 2002 Feb;49(1):1-18. Dan Med Bull. 2002. PMID: 11894721 Review.
Cited by
-
Three years of alendronate treatment does not continue to decrease microstructural stresses and strains associated with trabecular microdamage initiation beyond those at 1 year.Osteoporos Int. 2012 Sep;23(9):2313-20. doi: 10.1007/s00198-011-1875-8. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Osteoporos Int. 2012. PMID: 22237815
-
The effects of bisphosphonates on jaw bone remodeling, tissue properties, and extraction healing.Odontology. 2011 Jan;99(1):8-17. doi: 10.1007/s10266-010-0153-0. Epub 2011 Jan 27. Odontology. 2011. PMID: 21271320 Review.
-
Proximal femoral reconstruction for failed internal fixation of a bisphosphonate-related femur fracture.Arthroplast Today. 2016 Aug 24;2(4):153-156. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2016.04.001. eCollection 2016 Dec. Arthroplast Today. 2016. PMID: 28326420 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical femoral fractures, bisphosphonates, and mechanical stress.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2014 Jun;12(2):189-93. doi: 10.1007/s11914-014-0200-9. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2014. PMID: 24615358
-
Impending Atypical Femoral Fracture on the Contralateral Side Progressed to a Complete Fracture Early after Surgery for an Atypical Femoral Fracture: A Case Report.J Orthop Case Rep. 2024 Jun;14(6):135-139. doi: 10.13107/jocr.2024.v14.i06.4530. J Orthop Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38911004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen MR, Iwata K, Phipps R, Burr DB. Alterations in canine vertebral bone turnover, microdamage accumulation, and biomechanical properties following 1-year treatment with clinical treatment doses of risedronate or alendronate. Bone. 2006;39:872–879. - PubMed
-
- Mashiba T, Turner CH, Hirano T, Forwood MR, Johnston CC, Burr DB. Effects of suppressed bone turnover by bisphosphonates on microdamage accumulation and biomechanical properties in clinically relevant skeletal sites in beagles. Bone. 2001;28:524–531. - PubMed
-
- Allen MR, Burr DB. Three years of alendronate treatment results in similar levels of vertebral microdamage as after one year of treatment. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22:1759–1765. - PubMed
-
- Komatsubara S, Mori S, Mashiba T, Ito M, Li J, Kaji Y, Akiyama T, Miyamoto K, Cao Y, Kawanishi J, Norimatsu H. Long-term treatment of incadronate disodium accumulates microdamage but improves the trabecular bone microarchitecture in dog vertebra. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18:512–520. - PubMed
-
- Mashiba T, Hirano T, Turner CH, Forwood MR, Johnston CC, Burr DB. Suppressed bone turnover by bisphosphonates increases microdamage accumulation and reduces some biomechanical properties in dog rib. J Bone Miner Res. 2000;15:613–620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

