A review of effective interventions for reducing aggression and violence
- PMID: 18467276
- PMCID: PMC2606715
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0035
A review of effective interventions for reducing aggression and violence
Abstract
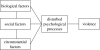
This paper addresses the question of whether individual violence can be reduced in frequency or severity, if so to what extent and by which methods. It opens with a brief overview of the nature of personal violence and discussion of some key definitional and methodological problems. However, its principal focus is on the findings obtained from a series of meta-analytic reviews of structured programmes for adolescents and adults who have shown repeated aggression or been convicted of personal violence, drawing together the results of studies conducted in prison, probation, youth justice and allied services. Additional results are considered from a systematic review of studies of violence prevention among offenders with mental disorders. This incorporates the preliminary findings of a meta-analysis of controlled trials of psychosocial interventions with that population. Overall, it is concluded that there is sufficient evidence currently available to substantiate the claim that personal violence can be reduced by psychosocial interventions, but that much more research is required to delineate the parameters of effectiveness in this context. Proposals are made for future investigations with reference to the theoretical understanding of causal relationships and the design of experimental trials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Psychological and/or educational interventions for the prevention of depression in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(1):CD003380. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003380.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Dec 07;(12):CD003380. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003380.pub3. PMID: 14974014 Updated.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Parent-training programmes for improving maternal psychosocial health.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(1):CD002020. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002020.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jun 13;(6):CD002020. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002020.pub3. PMID: 14973981 Updated.
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interventions targeted at women to encourage the uptake of cervical screening.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 6;9(9):CD002834. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002834.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34694000 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gene expression profiles underlying aggressive behavior in the prefrontal cortex of cattle.BMC Genomics. 2021 Apr 7;22(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07505-5. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33827428 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment Gain in Violent Offenders: The Relationship Between Proximal Outcomes, Risk Reduction and Violent Recidivism.Psychiatr Psychol Law. 2016 Aug 3;24(2):244-258. doi: 10.1080/13218719.2016.1209804. eCollection 2017. Psychiatr Psychol Law. 2016. PMID: 31983952 Free PMC article.
-
Aggression, Aggression-Related Psychopathologies and Their Models.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Jul 4;16:936105. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.936105. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35860723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide analyses of aggressiveness in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2016 Jul;171(5):733-47. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32434. Epub 2016 Mar 29. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2016. PMID: 27021288 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Prescription of Major Psychotropic Medications and Violent Reoffending After Prison Release.JAMA. 2016 Nov 1;316(17):1798-1807. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.15380. JAMA. 2016. PMID: 27802545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander M.A. Sexual offender treatment efficacy revisited. Sexual Abuse J. Res.Treat. 1999;11:101–116. doi:10.1007/BF02658841 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anderson C.A, Bushman B.J. Human aggression. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2002;53:27–51. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.53.100901.135231 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andrews D.A. Principles of effective correctional programs. In: Motiuk L.L, Serin R.C, editors. Compendium 2000 on effective correctional programming. Correctional Service Canada; Ottawa, Canada: 2001. pp. 9–17.
-
- Andrews D.A, Bonta J. 4th edn. LexisNexis/Anderson Publishing Co; Cincinnati, OH: 2006. The psychology of criminal conduct.
-
- Andrews D.A, Dowden C. Managing correctional treatment for reduced recidivism: a meta-analytic review of programme integrity. Legal Criminol. Psychol. 2005;10:173–187. doi:10.1348/135532505X36723 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources