Biologic features and treatment outcome of secondary acute lymphoblastic leukemia--a review of 101 cases
- PMID: 18467310
- PMCID: PMC2733065
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdn182
Biologic features and treatment outcome of secondary acute lymphoblastic leukemia--a review of 101 cases
Abstract
Background: Secondary acute lymphoblastic leukemia (sALL) is a rare disease and its biologic features are not well characterized.
Patients and methods: We describe a cohort of seven patients and discuss 94 additional cases from the literature for whom biological parameters were described. Cases with incomplete data were excluded.
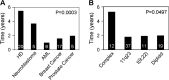
Results: Hodgkin's disease (HD) was more common in the 18-59 age group while breast and prostate cancers were prevalent only in the >or=18-year-old patients. The time interval to develop sALL was similar among all age groups but was significantly longer for HD and neuroblastoma primary diagnoses and sALL with complex karyotype. T-cell immunophenotype was more common in the <18 age group. Complete remission was infrequent in the >or=60 age group. The overall survival was poor for all sALL regardless of age, primary diagnoses, cytogenetic subgroups, or immunophenotype. Allogeneic transplantation most probably represents the only chance of cure.
Conclusion: Better identification of prognostic factors to prevent the occurrence of sALL is indicated.
Figures
References
-
- Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Diebold J, et al. World Health Organization classification of neoplastic diseases of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues: report of the Clinical Advisory Committee meeting-Airlie House, Virginia, November 1997. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:3835–3849. - PubMed
-
- Pagano L, Pulsoni A, Tosti ME, et al. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia occurring as second malignancy: report of the GIMEMA archive of adult acute leukaemia. Gruppo Italiano Malattie Ematologiche Maligne dell'Adulto. Br J Haematol. 1999;106:1037–1040. - PubMed
-
- Petit B, Mele L, Rack K, et al. Characteristics of secondary acute lymphoblastic leukemia with L3 morphology in adult patients. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002;43:1599–1604. - PubMed
-
- Boerma EG, van Imhoff GW, Appel IM, et al. Gender and age-related differences in Burkitt lymphoma—epidemiological and clinical data from The Netherlands. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40:2781–2787. - PubMed
-
- Stass S, Mirro J, Melvin S, et al. Lineage switch in acute leukemia. Blood. 1984;64:701–706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

