Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated suppression of adipocyte apolipoprotein E gene transcription: primary role for the nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB pathway and NFkappaB p50
- PMID: 18467438
- PMCID: PMC2488247
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2008-0340
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated suppression of adipocyte apolipoprotein E gene transcription: primary role for the nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB pathway and NFkappaB p50
Abstract
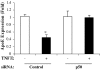
The adipose tissue inflammation accompanying obesity has important consequences for adipocyte lipid metabolism, and increased adipose tissue TNFalpha plays an important role for mediating the effect of inflammation on adipocyte function. Recent studies have shown that apolipoprotein E (apoE) is highly expressed in adipose tissue where it plays an important role in modulating adipocyte triglyceride metabolism, triglyceride mass, and adipocyte size. We have previously reported that TNFalpha reduces adipocyte apoE, and the current studies were undertaken to evaluate the molecular mechanism for this regulation. TNFalpha repression of adipocyte apoE gene expression required an intact nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB binding site at -43 in the apoE promoter. Site-directed mutagenesis at this site completely eliminated TNFalpha regulation of an apoE gene reporter. TNFalpha treatment activated binding of NFkappaB p50, isolated from adipocyte nuclei, to the apoE promoter. Two structurally distinct inhibitors of NFkappaB complex activation or translocation abrogated the TNFalpha effect on the apoE gene. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation assays, we demonstrated that treatment of adipocytes with TNFalpha led to increased binding of NFkappaB p50, and decreased binding of p65 and Sp1, to this region of the apoE promoter in living cells. The key role played by increased p50 binding was confirmed by p50 knockdown experiments. Reduction of p50 expression using small interference RNA completely eliminated TNFalpha-mediated reduction of endogenous adipocyte apoE gene expression. These results establish the molecular link between adipose tissue inflammation and apoE gene expression in adipocytes. The suppression of adipocyte apoE by the proinflammatory adipose tissue milieu associated with obesity will have important downstream effects on adipocyte triglyceride turnover and content.
Figures
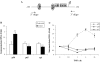
Similar articles
-
Oxidative stress regulates adipocyte apolipoprotein e and suppresses its expression in obesity.Diabetes. 2008 Nov;57(11):2992-8. doi: 10.2337/db08-0592. Epub 2008 Aug 4. Diabetes. 2008. PMID: 18678613 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor {gamma} stimulation of adipocyte ApoE gene transcription mediated by the liver receptor X pathway.J Biol Chem. 2009 Apr 17;284(16):10453-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808482200. Epub 2009 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19218241 Free PMC article.
-
Thymoquinone attenuates proinflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-activated mast cells by modulating NF-kappaB nuclear transactivation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Apr;1770(4):556-64. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2007.01.002. Epub 2007 Jan 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17292554
-
Insights into the roles of Apolipoprotein E in adipocyte biology and obesity.Int J Obes (Lond). 2024 Sep;48(9):1205-1215. doi: 10.1038/s41366-024-01549-9. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Int J Obes (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38839985 Review.
-
Apolipoprotein E synthesized by adipocyte and apolipoprotein E carried on lipoproteins modulate adipocyte triglyceride content.Lipids Health Dis. 2014 Aug 23;13:136. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-13-136. Lipids Health Dis. 2014. PMID: 25148848 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism for endogenously expressed ApoE modulation of adipocyte very low density lipoprotein metabolism: role in endocytic and lipase-mediated metabolic pathways.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 13;284(46):31512-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.004754. Epub 2009 Sep 18. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19767394 Free PMC article.
-
m6A mRNA Methylation Regulates Epithelial Innate Antimicrobial Defense Against Cryptosporidial Infection.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 6;12:705232. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.705232. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34295340 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected human monocytes down-regulate microglial MMP-2 secretion in CNS tuberculosis via TNFα, NFκB, p38 and caspase 8 dependent pathways.J Neuroinflammation. 2011 May 11;8:46. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-46. J Neuroinflammation. 2011. PMID: 21569377 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of chronic state of inflammation as mediators that link obese adipose tissue and metabolic syndrome.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:136584. doi: 10.1155/2013/136584. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 23843680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous adipocyte apolipoprotein E is colocalized with caveolin at the adipocyte plasma membrane.J Lipid Res. 2011 Mar;52(3):489-98. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M011809. Epub 2010 Dec 16. J Lipid Res. 2011. PMID: 21169230 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scherer PE 2006 Adipose tissue: from lipid storage compartment to endocrine organ. Diabetes 55:1537–1545 - PubMed
-
- Fantuzzi G, Mazzone T 2007 Adipose tissue and atherosclerosis: exploring the connection. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:996–1003 - PubMed
-
- Berg AH, Scherer PE 2005 Adipose tissue, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res 96:939–949 - PubMed
-
- Bluher M, Wilson-Fritch L, Lezyki J, Lausten PG, Corvera S, Kahn R 2004 Role of insulin action and cell size on protein expression patterns in adipocytes. J Biol Chem 279:31902–31909 - PubMed
-
- Kershaw EE, Flier JS 2004 Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2548–2556 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

