Regulation of transforming growth factor beta-induced responses by protein kinase A in pancreatic acinar cells
- PMID: 18467503
- PMCID: PMC2494718
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00492.2007
Regulation of transforming growth factor beta-induced responses by protein kinase A in pancreatic acinar cells
Abstract
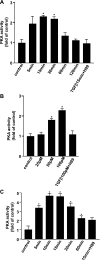
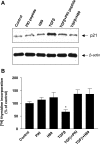
TGF-beta is an important regulator of growth and differentiation in the pancreas and has been implicated in pancreatic tumorigenesis. We have recently demonstrated that TGF-beta can activate protein kinase A (PKA) in mink lung epithelial cells (Zhang L, Duan C, Binkley C, Li G, Uhler M, Logsdon C, Simeone D. Mol Cell Biol 24: 2169-2180, 2004). In this study, we sought to determine whether TGF-beta activates PKA in pancreatic acinar cells, the mechanism by which PKA is activated, and PKA's role in TGF-beta-mediated growth regulatory responses. TGF-beta rapidly activated PKA in pancreatic acini while having no effect on intracellular cAMP levels. Coimmunoprecipitation experiments demonstrated a physical interaction between a Smad3/Smad4 complex and the regulatory subunits of PKA. TGF-beta also induced activation of the PKA-dependent transcription factor CREB. Both the specific PKA inhibitor H89 and PKI peptide significantly blocked TGF-beta's ability to activate PKA and CREB. TGF-beta-mediated growth inhibition and TGF-beta-induced p21 and SnoN expression in pancreatic acinar cells were blocked by H89 and PKI peptide. This study demonstrates that this novel cross talk between TGF-beta and PKA signaling pathways may play an important role in regulating TGF-beta signaling in the pancreas.
Figures
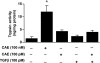




Similar articles
-
Protein kinase A modulates transforming growth factor-β signaling through a direct interaction with Smad4 protein.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 22;288(12):8737-8749. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.455675. Epub 2013 Jan 28. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23362281 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-elevating agents inhibit transforming growth factor-beta-induced SMAD3/4-dependent transcription via a protein kinase A-dependent mechanism.Oncogene. 2003 Dec 4;22(55):8881-90. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206871. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 14654784
-
A transforming growth factor beta-induced Smad3/Smad4 complex directly activates protein kinase A.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Mar;24(5):2169-80. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.5.2169-2180.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14966294 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating biological risk factors in suicide: role of protein kinase A.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011 Jun 1;35(4):831-41. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.08.025. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 20817068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Kinase Inhibitor Peptide as a Tool to Specifically Inhibit Protein Kinase A.Front Physiol. 2020 Nov 25;11:574030. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.574030. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33324237 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein Kinase A Inhibitor H89 Attenuates Experimental Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Feb 7;61(2):1. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.2.1. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32031573 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulatory Effects of Transforming Growth Factor-β on Nerve Regeneration.Cell Transplant. 2017 Mar 13;26(3):381-394. doi: 10.3727/096368916X693824. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Cell Transplant. 2017. PMID: 27983926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGFβ-Induced Lung Cancer Cell Migration Is NR4A1-Dependent.Mol Cancer Res. 2018 Dec;16(12):1991-2002. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-18-0366. Epub 2018 Aug 2. Mol Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30072581 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP and Epac in the regulation of tissue fibrosis.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 May;166(2):447-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01847.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22233238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Requirement for protein kinase A in the phosphorylation of the TGFβ receptor-interacting protein km23-1 as a component of TGFβ downstream effects.Exp Cell Res. 2013 Apr 1;319(6):897-907. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.12.029. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Exp Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23333499 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bakin AV, Tomlinson AK, Bhowmick NA, Moses HL, Arteaga CL. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase function is required for transforming growth factor beta-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cell migration. J Biol Chem 275: 36803–36810, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya E, Panchal A, Wilkins TJ, de Ondarza J, Hootman SR. Insulin, transforming growth factors, and substrates modulate growth of guinea pig pancreatic duct cells in vitro. Gastroenterology 109: 944–952, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Bhowmick NA, Zent R, Ghiassi M, McDonnell M, Moses HL. Integrin beta 1 signaling is necessary for transforming growth factor-beta activation of p38MAPK and epithelial plasticity. J Biol Chem 276: 46707–46713, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Bottinger EP, Jakubczak JL, Roberts IS, Mumy M, Hemmati P, Bagnall K, Merlino G, Wakefield LM. Expression of a dominant-negative mutant TGF-beta type II receptor in transgenic mice reveals essential roles for TGF-beta in regulation of growth and differentiation in the exocrine pancreas. EMBO J 16: 2621–2633, 1997. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boyton AL, Whitfield JF. The role of cAMP in cell proliferation: a critical assessment of the evidence. In: Advances in Cyclic Nucleotide Research (vol. 15), edited by Greengard P and Robison GA. New York: Raven, 1983, p. 193–294.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

