CD19 regulates skin and lung fibrosis via Toll-like receptor signaling in a model of bleomycin-induced scleroderma
- PMID: 18467694
- PMCID: PMC2408424
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.071049
CD19 regulates skin and lung fibrosis via Toll-like receptor signaling in a model of bleomycin-induced scleroderma
Abstract
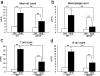
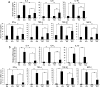
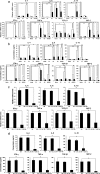
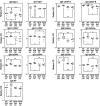
Mice subcutaneously injected with bleomycin, in an experimental model of human systemic sclerosis, develop cutaneous and lung fibrosis with autoantibody production. CD19 is a general "rheostat" that defines signaling thresholds critical for humoral immune responses, autoimmunity, and cytokine production. To determine the role of CD19 in the bleomycin-induced systemic sclerosis model, we investigated the development of fibrosis and autoimmunity in CD19-deficient mice. Bleomycin-treated wild-type mice exhibited dermal and lung fibrosis, hyper-gamma-globulinemia, autoantibody production, and enhanced serum and skin expression of various cytokines, including fibrogenic interleukin-4, interleukin-6, and transforming growth factor-beta1, all of which were inhibited by CD19 deficiency. Bleomycin treatment enhanced hyaluronan production in the skin, lung, and sera. Addition of hyaluronan, an endogenous ligand for Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR4, stimulated B cells to produce various cytokines, primarily through TLR4; CD19 deficiency suppressed this stimulation. These results suggest that bleomycin induces fibrosis by enhancing hyaluronan production, which activates B cells to produce fibrogenic cytokines mainly via TLR4 and induce autoantibody production, and that CD19 deficiency suppresses fibrosis and autoantibody production by inhibiting TLR4 signals.
Figures

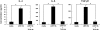

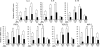

References
-
- LeRoy EC, Krieg T, Black C, Medsger TAJ, Fleischmajer R, Rowell N, Jablonska S, Wollheim F. Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets, and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol. 1988;15:202–205. - PubMed
-
- Okano Y. Antinuclear antibody in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1996;22:709–735. - PubMed
-
- Sato S, Fujimoto M, Hasegawa M, Takehara K. Altered blood B lymphocyte homeostasis in systemic sclerosis: expanded naive B cells and diminished but activated memory B cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:1918–1927. - PubMed
-
- Gudbjornsson B, Hallgren R, Nettelbladt O, Gustafsson R, Mattsson A, af Geijerstam E, Totterman TH. Phenotypic and functional activation of alveolar macrophages. T lymphocytes and NK cells in patients with systemic sclerosis and primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994;53:574–579. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

