Neurogenesis and alterations of neural stem cells in mouse models of cerebral amyloidosis
- PMID: 18467698
- PMCID: PMC2408413
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.060520
Neurogenesis and alterations of neural stem cells in mouse models of cerebral amyloidosis
Abstract
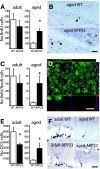
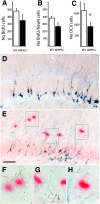
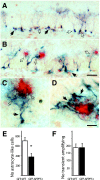
The hippocampus in Alzheimer's disease is burdened with amyloid plaques and is one of the few locations where neurogenesis continues throughout adult life. To evaluate the impact of amyloid-beta deposition on neural stem cells, hippocampal neurogenesis was assessed using bromodeoxyuridine incorporation and doublecortin staining in two amyloid precursor protein (APP) transgenic mouse models. In 5-month-old APP23 mice prior to amyloid deposition, neurogenesis showed no robust difference relative to wild-type control mice, but 25-month-old amyloid-depositing APP23 mice showed significant increases in neurogenesis compared to controls. In contrast, 8-month-old amyloid-depositing APPPS1 mice revealed decreases in neurogenesis compared to controls. To study whether alterations in neurogenesis are the result of amyloid-induced changes at the level of neural stem cells, APPPS1 mice were crossed with mice expressing green fluorescence protein (GFP) under a central nervous system-specific nestin promoter. Eight-month-old nestin-GFP x APPPS1 mice exhibited decreases in quiescent nestin-positive astrocyte-like stem cells, while transient amplifying progenitor cells did not change in number. Strikingly, both astrocyte-like and transient-amplifying progenitor cells revealed an aberrant morphologic reaction toward congophilic amyloid-deposits. A similar reaction toward the amyloid was no longer observed in doublecortin-positive immature neurons. Results provide evidence for a disruption of neural stem cell biology in an amyloidogenic environment and support findings that neurogenesis is differently affected among various transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer's disease.
Figures
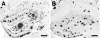
References
-
- Luskin MB. Restricted proliferation and migration of postnatally generated neurons derived from the forebrain subventricular zone. Neuron. 1993;11:173–189. - PubMed
-
- Doetsch F, Caille I, Lim DA, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A. Subventricular zone astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain. Cell. 1999;97:703–716. - PubMed
-
- Bondolfi L, Ermini F, Long JM, Ingram DK, Jucker M. Impact of age and caloric restriction on neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of C57BL/6 mice. Neurobiol Aging. 2004;25:333–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

