Proteasome inhibitors induce apoptosis of prostate cancer cells by inducing nuclear translocation of IkappaBalpha
- PMID: 18468507
- PMCID: PMC2574911
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2008.04.026
Proteasome inhibitors induce apoptosis of prostate cancer cells by inducing nuclear translocation of IkappaBalpha
Abstract
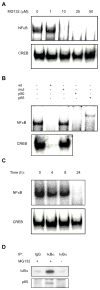
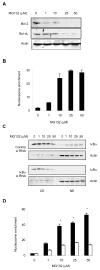
Proteasome inhibitors are known to suppress the proteasome-mediated degradation of IkappaBalpha in stimulated cells. This results in the cytoplasmic retention of NFkappaB and its reduced nuclear transcriptional activity. In this study, we show that in the metastatic prostate cancer cells, the proteasome inhibitors exhibit a novel, previously unrecognized effect: they increase the cellular levels of IkappaBalpha, which then translocates to the nucleus, associates with the nuclear p65 NFkappaB, thus inhibiting the constitutive NFkappaB DNA binding activity and inducing apoptosis. The proteasome inhibition-induced nuclear translocation of IkappaBalpha is dependent on de novo protein synthesis, occurs also in other cell types, and does not require IkappaBalpha phosphorylation on Ser-32. Since NFkappaB activity is constitutively increased in many human cancers as well as in inflammatory disorders, the proteasome inhibition-induced nuclear translocation of IkappaBalpha could thus provide a new therapeutic strategy aimed at the specific inhibition of NFkappaB activity by the nuclear IkappaBalpha.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prevention of etoposide-induced apoptosis by proteasome inhibitors in a human leukemic cell line but not in fresh acute leukemia blasts. A differential role of NF-kappab activation.Biochem Pharmacol. 2000 Sep 15;60(6):823-30. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(00)00387-7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10930537
-
Bcl-2 activates the transcription factor NFkappaB through the degradation of the cytoplasmic inhibitor IkappaBalpha.J Biol Chem. 1998 Sep 11;273(37):23946-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.37.23946. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9727009
-
Proteasome inhibitors impair RANKL-induced NF-kappaB activity in osteoclast-like cells via disruption of p62, TRAF6, CYLD, and IkappaBalpha signaling cascades.J Cell Physiol. 2009 Aug;220(2):450-9. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21787. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19365810
-
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay analysis of NFκB transcriptional regulation by nuclear IκBα.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;809:49-62. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-376-9_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22113267
-
Suppression of constitutive and tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB activation and induction of apoptosis by apigenin in human prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells: correlation with down-regulation of NF-kappaB-responsive genes.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 May 1;10(9):3169-78. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-03-0586. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15131058
Cited by
-
Cancer biomarker discovery: the entropic hallmark.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 18;5(8):e12262. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012262. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20805891 Free PMC article.
-
Bcl3 regulates pro-survival and pro-inflammatory gene expression in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Nov;1843(11):2620-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.07.012. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 25089799 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical evaluation of 4-[3,5-bis(2-chlorobenzylidene)-4-oxo-piperidine-1-yl]-4-oxo-2-butenoic acid, in a mouse model of lung cancer xenograft.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec;170(7):1436-48. doi: 10.1111/bph.12406. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24102070 Free PMC article.
-
NFκB function and regulation in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.Am J Cancer Res. 2013 Nov 1;3(5):433-45. Am J Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24224122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRIM13 (RFP2) downregulation decreases tumour cell growth in multiple myeloma through inhibition of NF Kappa B pathway and proteasome activity.Br J Haematol. 2013 Jul;162(2):210-20. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12365. Epub 2013 May 7. Br J Haematol. 2013. PMID: 23647456 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

