Recent progress in antiretrovirals--lessons from resistance
- PMID: 18468560
- PMCID: PMC2581412
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2008.02.003
Recent progress in antiretrovirals--lessons from resistance
Abstract
Recent failures in efforts to develop an effective vaccine against HIV-1 infection have emphasized the importance of antiretroviral therapy in treating HIV-1-infected patients. Thus far, inhibitors of two viral enzymes, reverse transcriptase and protease, have had a profoundly positive impact on the survival of HIV-1-infected patients. However, new inhibitors that act at diverse steps in the viral replication cycle are urgently needed because of the development of resistance to currently available antiretrovirals. This review summarizes recent progress in antiretroviral drug discovery and development by specifically focusing on novel inhibitors of three phases of replication: viral entry, integration of the viral DNA into the host cell genome and virus particle maturation.
Figures
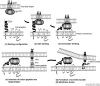
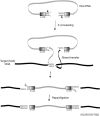
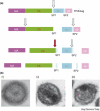
References
-
- UNAIDS . Report on the Global HIV/AIDS Epidemic. UNAIDS; 2006.
-
- Rambaut A, et al. The causes and consequences of HIV evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004;5:52–61. - PubMed
-
- Hu WS, et al. Retroviral recombination: review of genetic analyses. Front. Biosci. 2003;8:d143–d155. - PubMed
-
- Najera R, et al. Genetic recombination and its role in the development of the HIV-1 pandemic. AIDS. 2002;16(Suppl 4):S3–S16. - PubMed
-
- Thomson MM, et al. Molecular epidemiology of HIV-1 genetic forms and its significance for vaccine development and therapy. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2002;2:461–471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

