Inhibition of alphavirus infection in cell culture and in mice with antisense morpholino oligomers
- PMID: 18468653
- PMCID: PMC2447162
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.03.032
Inhibition of alphavirus infection in cell culture and in mice with antisense morpholino oligomers
Abstract
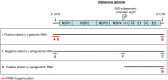
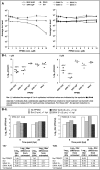
The genus Alphavirus contains members that threaten human health, both as natural pathogens and as potential biological weapons. Peptide-conjugated phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers (PPMO) enter cells readily and can inhibit viral replication through sequence-specific steric blockade of viral RNA. Sindbis virus (SINV) has low pathogenicity in humans and is regularly utilized as a model alphavirus. PPMO targeting the 5'-terminal and AUG translation start site regions of the SINV genome blocked the production of infectious SINV in tissue culture. PPMO designed against corresponding regions in Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (VEEV) were likewise found to be effective in vitro against several strains of VEEV. Mice treated with PPMO before and after VEEV infection were completely protected from lethal outcome while mice receiving only post-infection PPMO treatment were partially protected. Levels of virus in tissue samples correlated with animal survival. Uninfected mice suffered no apparent ill-effects from PPMO treatment. Thus, PPMO appear promising as candidates for therapeutic development against alphaviruses.
Figures





References
-
- Abes S., Moulton H.M., Clair P., Prevot P., Youngblood D.S., Wu R.P., Iversen P.L., Lebleu B. Vectorization of morpholino oligomers by the (R-Ahx-R)(4) peptide allows efficient splicing correction in the absence of endosomolytic agents. J. Control. Release. 2006;116(3):304–313. - PubMed
-
- Berge T.O., Banks I.S., Tigertt W.D. Attenuation of Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus by in vitro cultivation in guinea pig heart cells. Am. J. Hyg. 1961;73:209–218.
-
- Caplen N.J., Zheng Z., Falgout B., Morgan R.A. Inhibition of viral gene expression and replication in mosquito cells by dsRNA-triggered RNA interference. Mol. Ther. 2002;6(2):243–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

