Photosynthetic generation of oxygen
- PMID: 18468983
- PMCID: PMC2606770
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0047
Photosynthetic generation of oxygen
Abstract
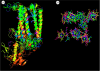
The oxygen in the atmosphere is derived from light-driven oxidation of water at a catalytic centre contained within a multi-subunit enzyme known as photosystem II (PSII). PSII is located in the photosynthetic membranes of plants, algae and cyanobacteria and its oxygen-evolving centre (OEC) consists of four manganese ions and a calcium ion surrounded by a highly conserved protein environment. Recently, the structure of PSII was elucidated by X-ray crystallography thus revealing details of the molecular architecture of the OEC. This structural information, coupled with an extensive knowledge base derived from a wide range of biophysical, biochemical and molecular biological studies, has provided a framework for understanding the chemistry of photosynthetic oxygen generation as well as opening up debate about its evolutionary origin.
Figures




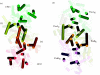
References
-
- Barber J. Photosynthetic reaction centres: a common link. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1987;12:321–326. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(87)90151-4. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

